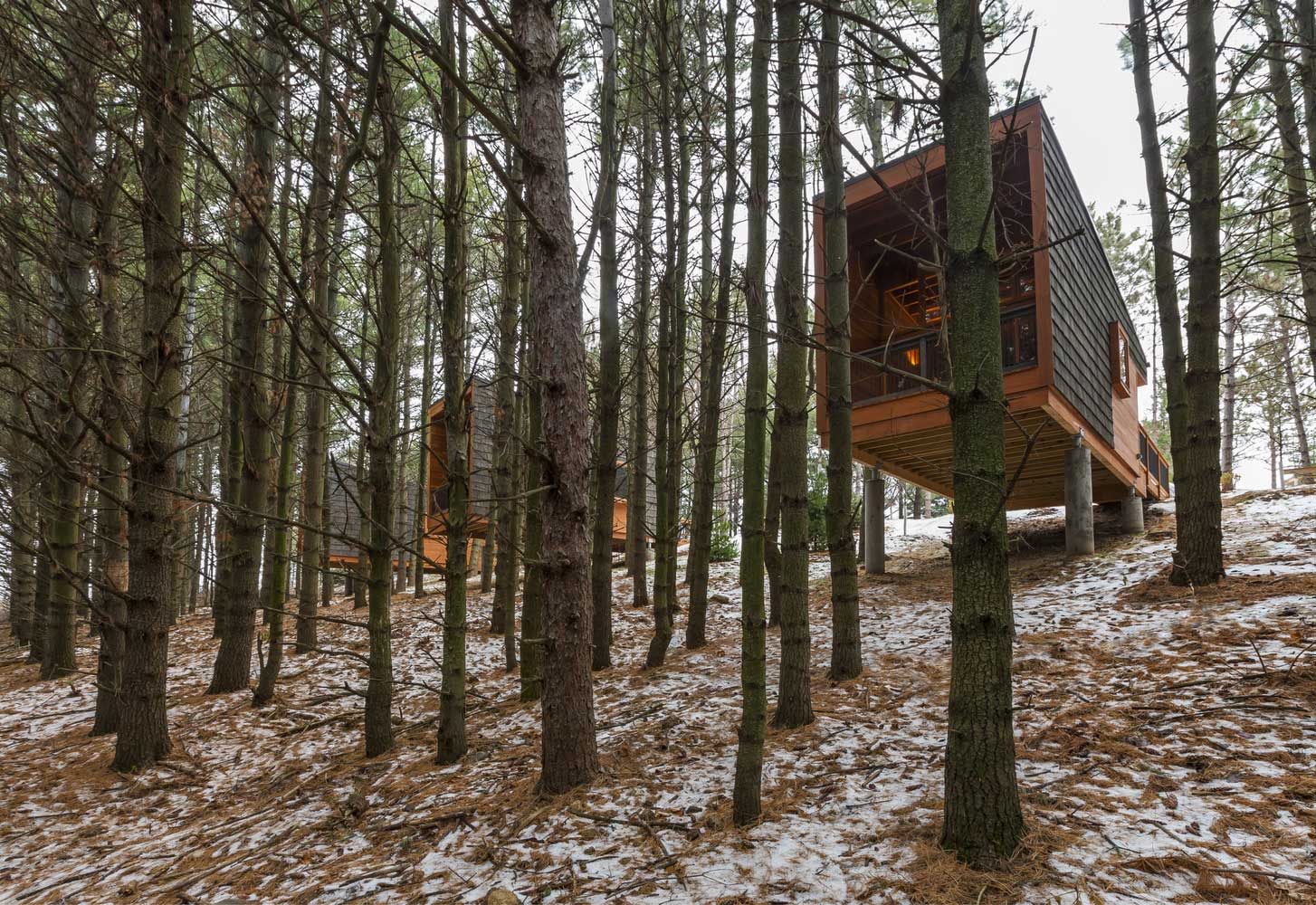
Wood in architecture, construction and works
The art of wood architecture is more alive than ever with a palpable trend for ecological building materials that respect the environment.
Modern wooden buildings are already a reality. Architects and designers use this noble material but with renovating techniques achieving sustainable buildings with spectacular design.
Did you know that 18% of the world’s population lives in houses built with wood?
Sustainable wood construction is having a positive impact on the end user; convenience, quality and comfort that other materials do not reach, but even more on the environment. Some examples
Wood as a sustainable material in architecture
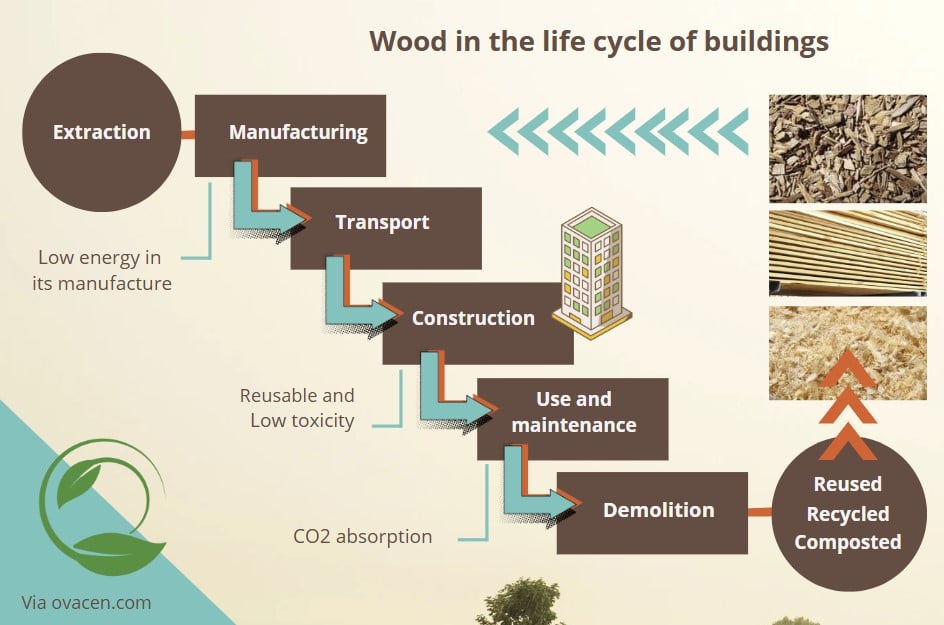
In the concern for the environment, wood is a sustainable option for building construction. It has a renewable and biodegradable life cycle that respects the planet? Why?
The simplest way to understand the environmental advantages of wood in the building cycle is to use the following diagram:
If we compare wood with other traditional building materials, we can quickly identify that we need to further expand its use in the architectural sector. The following table demonstrates this conclusively:
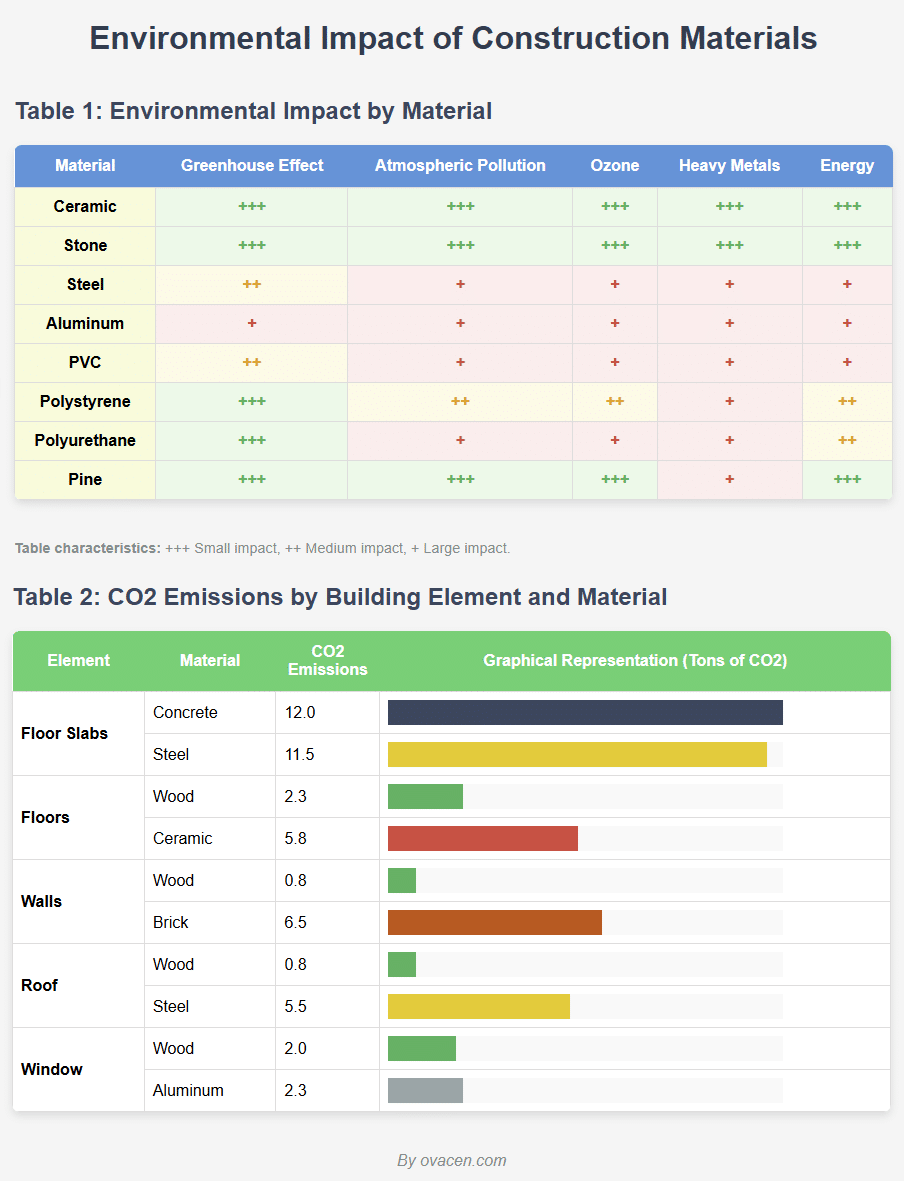
We must highlight and start to assume, that wood construction is the technique that best adapts and meets the energy efficiency standards in all regulations that support efficient and sustainable architecture.
In addition, there are different sustainable wood certifications to guarantee responsible sourcing, construction quality and environmentally correct management. Some examples are:
- Forest Stewardship Council (FSC): The website can be consulted HERE. Global in scope and possibly the best known certification, it evaluates forest management and offers three levels of certification.
- Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC): Regional emphasis, focuses on certification of national systems and offers two levels of certification.
- American Tree Farm Association (ATFA): U.S. focus, evaluates sustainable forestry practices and offers two levels of certification.
- PEFC Spain: Sustainable Forest Management (PEFC SW) and Chain of Custody (PEFC COC).
- Timber for Sustainable Construction (MCS): Spanish standard for structural use. A single level covering forest management and chain of custody.
The following video explores the future of wood in structures and its consequences. With interesting reflections!…
Advantages of wood in architecture
It should be noted that the advantages of wood are much greater than its disadvantages as a material.
| Advantage | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable | 100% renewable raw material when properly harvested and with the appropriate certificates. |
| Natural insulation | Provides natural thermal and acoustic insulation, reducing energy use in air conditioning. |
| Ease of handling | Versatile and easy-to-work material that allows for a variety of applications, from simple to complex. |
| Durability | When properly treated, wood provides a long service life. |
| Affordability | Easy to find and relatively inexpensive compared to other materials. |
| Versatility of form | Can be produced in structural dimensions of any size, adapting to multiple uses. |
| Reusable | Wood can be reused several times, minimizing waste. |
| Structural properties | High mechanical strength and flexibility, capable of resisting compressive and tensile loads. |
| Diversity of textures | Offers a wide variety of textures and finishes to add beauty and character to projects. |
- It is a natural product. It is a product of natural origin, recyclable and renewable, whose production process compared to other industrialized products offers less waste, requires low energy consumption and respects nature and the environment. The current use is non-toxic, does not produce odors or toxic vapors of chemical origin, therefore, it is safe to touch and handle. It is also an easy material to work with.
- It is 100% renewable if trees are harvested in the forests properly and with the appropriate certificates. New trees are planted carefully and without compromising natural resources.
- Good insulation. Insulation is a very important aspect for the reduction of energy used in heating and air conditioning of buildings. Wood is a natural insulator that can reduce the amount of energy needed for space heating and cooling, especially when used in windows, floors or doors. It has excellent natural thermal insulation and sound absorption properties.
- Ease of handling and structure. It is a very versatile raw material that can be used in a variety of ways and meets certain specifications and needs, according to the desired type of application. It leaves simple connections and splices to be executed up to complex structures with an adequate execution.
The oldest wooden house is in the town of Schwyz (Switzerland) and is 700 years old.
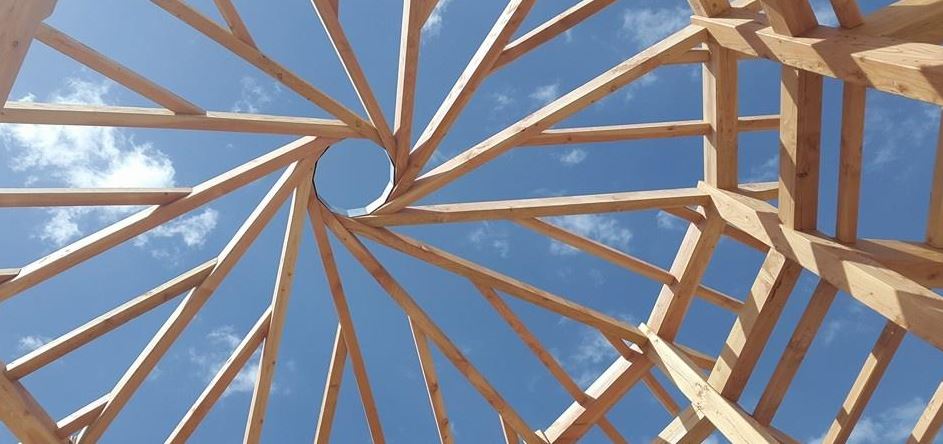

- A material that lasts. The use of wood in well-treated construction provides durability; a beam, a log or lath, or even a simple crossbeam needs maintenance. There are many examples of durability; sarcophagi, statues, family gear, weapons, boats, instruments, construction elements.
- Easy to find and relatively inexpensive compared to other materials.
- Utility of use with different shapes. It can be produced in pieces with structural dimensions of any size, it can be used in industrialization or in delicate elements.
- 100% reusable. Ability to be reused multiple times and without leftover material. (A perfect example is furniture with recycled pallets and how to make a geodesic dome).
- Structural properties. Able to withstand both compressive and tensile sacrifices. It has a low density, low mass and high mechanical strength. Flexural strength can be about ten times that of concrete. It does not crumble when subjected to sudden shocks that can cause damage to other building materials.
- Diversity of textures and finishes. In its natural appearance it offers an enormous plurality of patterns, whether smooth, wavy, rough…etc.
Disadvantages of wood in architecture
| Disadvantage | Brief Explanation |
|---|---|
| Variability in size | Sensitive to humidity changes. |
| Vulnerability | Susceptible to damage by water and other external elements. |
| Flammability | Highly flammable material. |
| Small size and dimensions | Limitations in size and dimensions. |
| Variability in strength and hardness | Strength and hardness depend on the type of wood. |
- Variability in size. It is highly sensitive to the environment, increasing or decreasing in size with changes in humidity.
- Vulnerability. Against attacks from external elements, for example water, its durability and hardness is limited when adequate precautionary measures are not taken.
- It is very fragile against fire, forming a “fuel element in the structures”. A good way to prevent possible adversities is with a fire detector or some type of smoke detector.
- Small size and dimensions if we work from an architectural perspective.
- Variability in strength and hardness. It is not the same the slats coming from the pine that the oak beams in a structure or for cutting, for example. It is necessary to look for its utility, technique and use for each function, whether for interior carpentry or decoration, for exterior, in structural framing … etc.
Physical and mechanical properties of wood
I would like to add a diagram with, first, a comparison with other building materials, and then a diagram of the mechanical properties of wood.
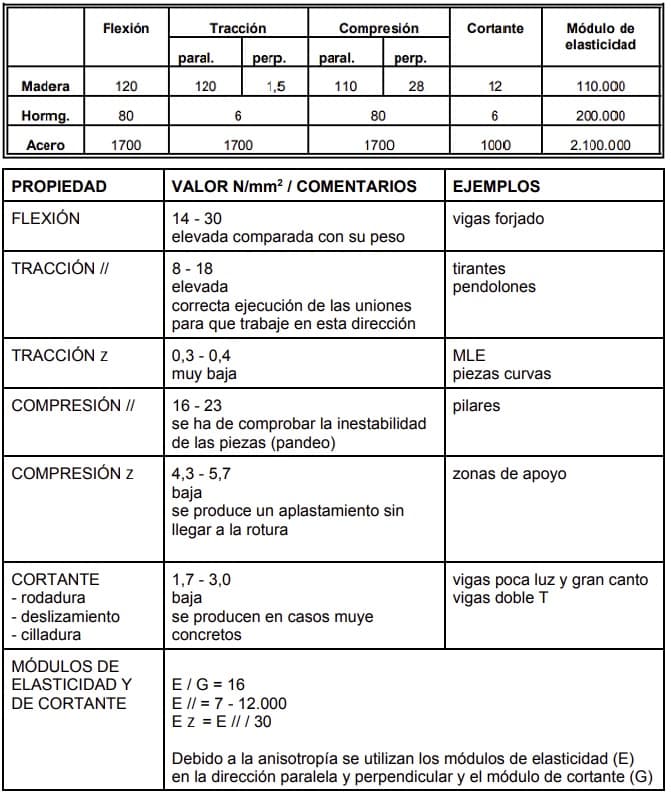
.
- The hardness: The resistance that presents being drilled with some metallic elements or certain machineries. This hardness is obtained in wood with little water content extracted from old trees.
- Density: Refers to its resistance, being subjected to bending or compression processes.
- Hygroscopicity: It is when it absorbs or gives off humidity by capillarity.
- Thermal and electrical conductivity: It is when it serves as an insulator in the field of electricity.
- Texture: refers to the physical that it presents, such as carvings, color, types of sanding … etc.
If you want more information about the characteristics of how it works in pillars, beams, foundations, etc… You can consult this manual from HERE. And we leave the following excellent video about the myths that circulate about this noble material:

Types of wood for construction
Although the current technology is providing a wide range of typologies where even extra materials are added that match perfectly, we can classify them in:
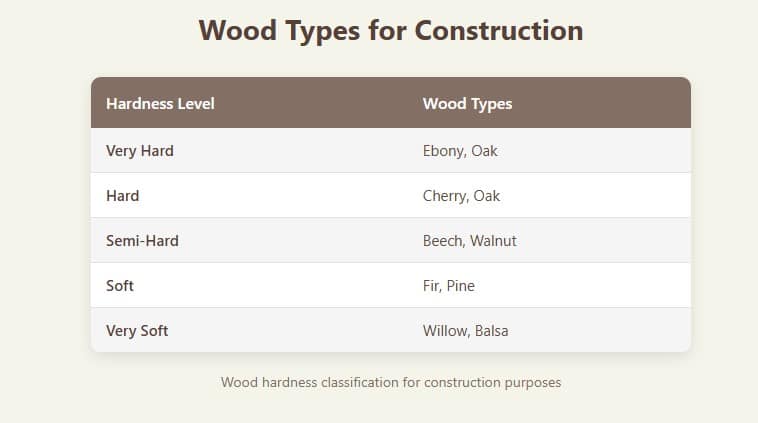
- M. Natural noble or hard. They are those heavy and resistant, which normally come from trees that have a slow growth (Examples such as Chestnut, Cherry, Ebony, Olive, Ash, Beech, Walnut, Oak …etc).
- M. Soft natural. The growth of the trees is much faster, so its resistances are softer and the sale of the same is more economical, at low prices in relation to the previous one. For example, it would enter the pine.
- Artificial wood. They are produced by means of chips or sheets suitably combined. This includes plywood, chipboard, fiberboard (DM and DB) and plywood.
In summary mode, we would mention the following types of wood for construction with the basic characteristics and their uses:
| Type of wood | Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Oak | Durable, resistant, rich in color | Structural construction, flooring, furniture |
| Cedar | Insect and rot resistant, light weight | Siding, roofing, garden furniture |
| Pine | Versatile, economical, easy to work with | Structures, siding, flooring |
| Walnut | Strong, attractive, moisture resistant | High quality furniture, paneling, flooring |
| Spruce | Light, strong, easy to work with | Structures, doors, windows |
| Mahogany | Durable, rot-resistant, attractive | High-end furniture, doors, windows |
| Teak | Moisture and insect resistant, durable | Outdoor furniture, decks |
| Bamboo | Sustainable, strong, flexible | Structures, furniture, flooring |
Innovations in wood technology
Innovation in wood technology has greatly expanded the possibilities of wood in contemporary architecture. Some of these innovations include laminating and microlaminating or thermally modified techniques. They improve strength and durability, allowing its use in an even wider range of architectural applications.
In the following list, some of the outstanding innovations are presented:
- Cross Laminated Timber (CLT): combines layers of wood to create strong, rigid panels.
- Cross Laminated Lumber (LSL, LVL): Formed from multiple layers of thin wood for superior strength and stiffness.
- Thermally Modified Lumber: Heat treats wood to improve its resistance to water and rot.
Wood architecture embraces innovation and reinvents itself thanks to technology Glued laminated timber (MLE), plywood and cross-laminated timber (CLT) are some examples of products that make it possible to create structures of great strength and lightness, opening up endless architectural possibilities.
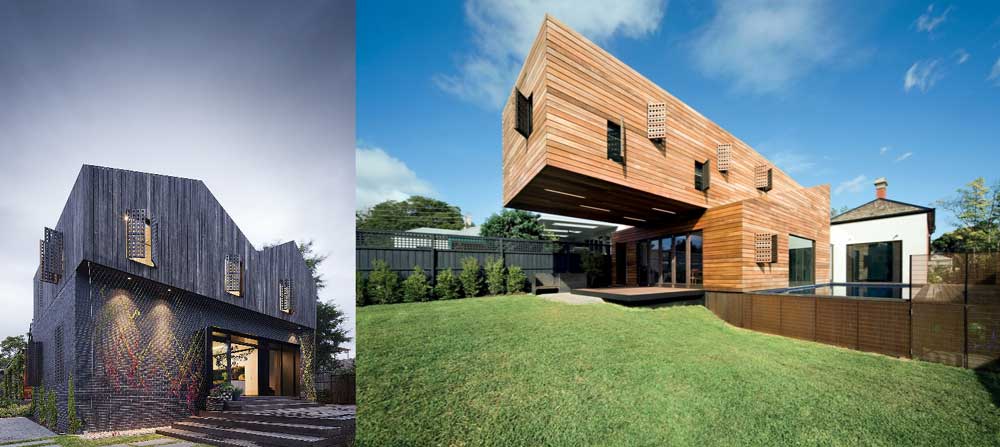

Some houses built with wood of which we could say…. I want one! It should be remembered that most wooden houses are made with prefabricated and modules.
In this sense we already spoke in the article of prefabricated houses that we shelled all the ins and outs of prefabricated wooden houses and other materials.
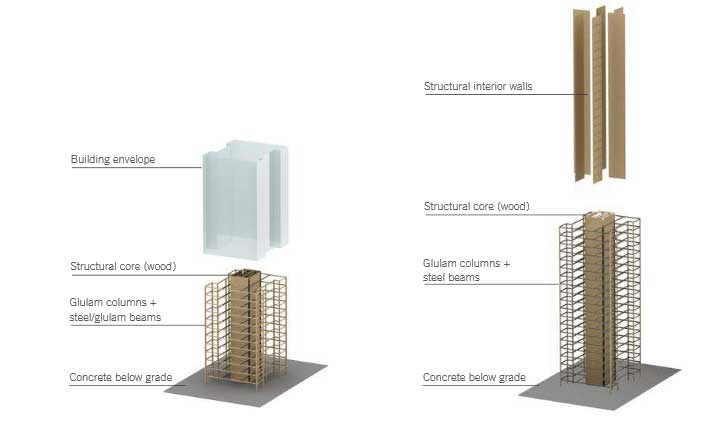
Wooden structure
Increasingly, designers are daring to use high-rise buildings and almost impossible wooden structures. As an example in Spain we can find it in the historic center of Lleida – holds the record for the tallest building in Spain – built with wood.
We leave you a video about the assembly of wooden structures for a multi-storey building (5 floors + first floor), at the end of the article there are different manuals and techniques for the construction of wooden houses:
Currently, the Forté Building in Melbourne stands as the tallest timber building in the world with 13 floors. This project by FJMT Architects stands out for its avant-garde design and commitment to sustainability.
The rest of the structure consists of a “beehive” of solid glulam panels that serve as load-bearing walls, enclosures, distribution and carpentry to form an exceptional framework. (More information about the company that is dedicated to build timber buildings from its projects HERE).
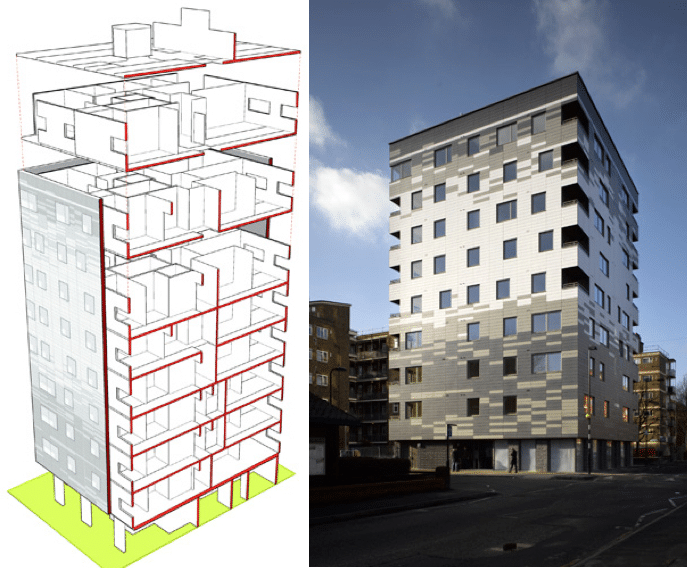
But the ability of architects is to surprise and in this case from the U.S. through the architectural firm Michael Green that proposes wooden skyscrapers, aiming to reach 20 floors, even raised to 30 floors (See also article on ranking of the world’s tallest skyscrapers).
A very risky idea where many detractors question the sustainability of the construction due to the high amount of raw material needed. The study gives us the complete project of how wooden skyscrapers should be built, see this PDF… With QUÍ information).
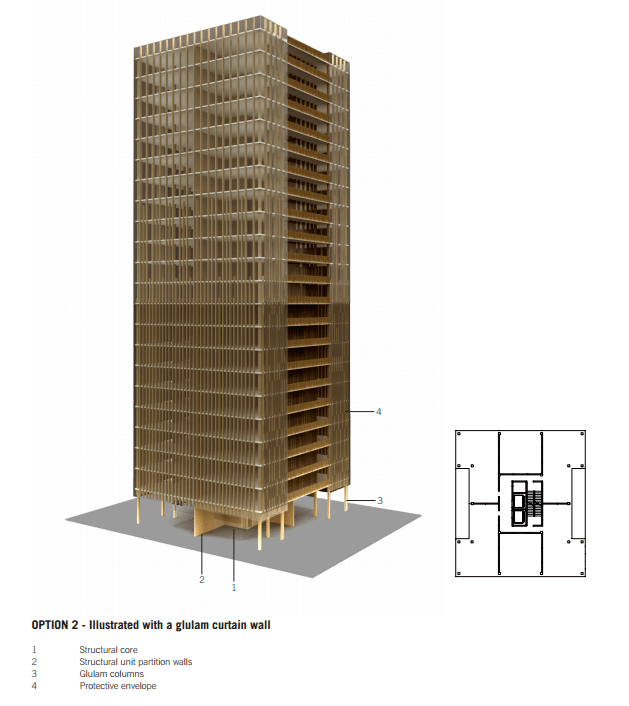
As in this case, we are lighter, and we wanted to compile a series of manuals or guides for construction and architecture in wood, houses, single-family homes, techniques on beams, sleepers, boards, joints, structures or to the understanding of the world of wood in the work…
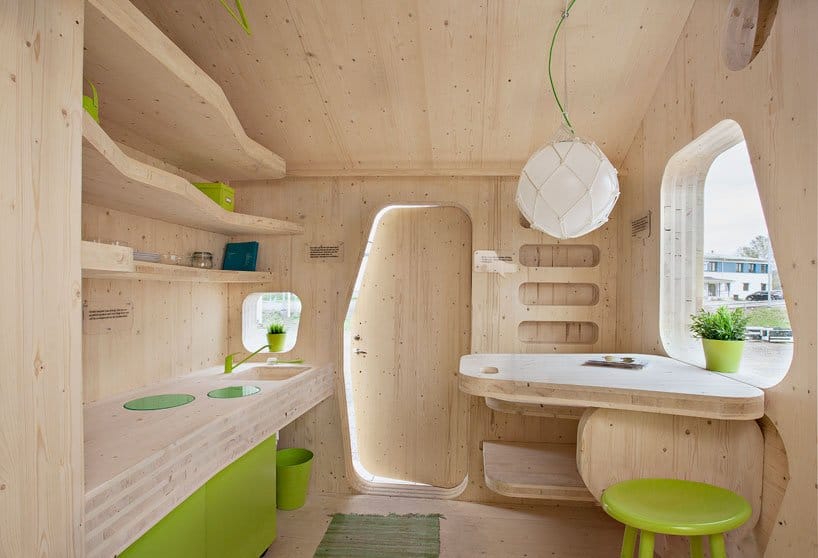

Wood construction and architecture manuals
- La construcción de viviendas en madera(Centro de Transferencia Tecnológica de la Madera CTT – Chile. With many chapters in PDF to learn.
- TABLE OF CONTENTS + INTRODUCTION
- Unit 1: WOOD
- Unit 2: PATHOLOGIES AND PROTECTION OF TIMBER IN SERVICE
- Unit 3: RELEVANT ASPECTS TO CONSIDER IN A HOUSING CONSTRUCTION PROJECT
- Unit 4: SAFETY AND RISK PREVENTION IN CONSTRUCTION
- Unit 5: TOOLS AND TOOLING TOOLS
- Unit 6: STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS
- Unit 7: FIXATIONS AND JOINTS
- Unit 8: FOUNDATIONS
- Unit 9: HORIZONTAL TRAMS
- Unit 10: VERTICAL FOUNDATIONS
- Unit 11: ROOF STRUCTURE
- Unit 12: STAIRS
- Unit 13: HABITABILITY ASPECTS
- Unit 14: INSULATION AND VENTILATION Unit 14: INSULATION AND VENTILATION
- Unit 15: FIRE PROTECTION
- Unit 16: CONSIDERATIONS IN THE DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF HOUSING FACILITIES Unit 16: HOUSING FACILITY CONSIDERATIONS
- Unit 17: WOODEN ROOFING SOLUTION
- Unit 18: WOODEN COVERINGS FOR EXTERIOR PARAMENTS Unit 19: WOODEN COVERING SOLUTION FOR EXTERIOR PARAMENTS
- Unit 19: ROOFING AND INTERIOR WALL PANELING SOLUTION
- Unit 20: WOODEN COVERINGS AS A FLOORING SOLUTION
- Unit 21: FINISHING WITH DECORATIVE WOOD MOLDINGS
- Unit 22: DOORS AND WINDOWS
- Unit 23: QUALITY MANAGEMENT
- APPENDIX 1
- APPENDIX 2
- APPENDIX 3
- ANNEX 4
- ANNEX 5
- ANNEX 6
- ANNEX 7
Access to all documents from HERE.
- Case study of a high-rise building constructed with wood from HERE PDF document.
- The subject of the joints in the structures on planks, boards and beams is complex, so much in the treatment of the cut, the edges as in the finishes of union, be for interior, exterior or in the own carpentry of a house. So, the following manual of wood construction is only about that, in fact they are schematic cards that although a little old are of great quality. Access from HERE (In the upper right side there are about 5 cards like the following, just click on the small images)
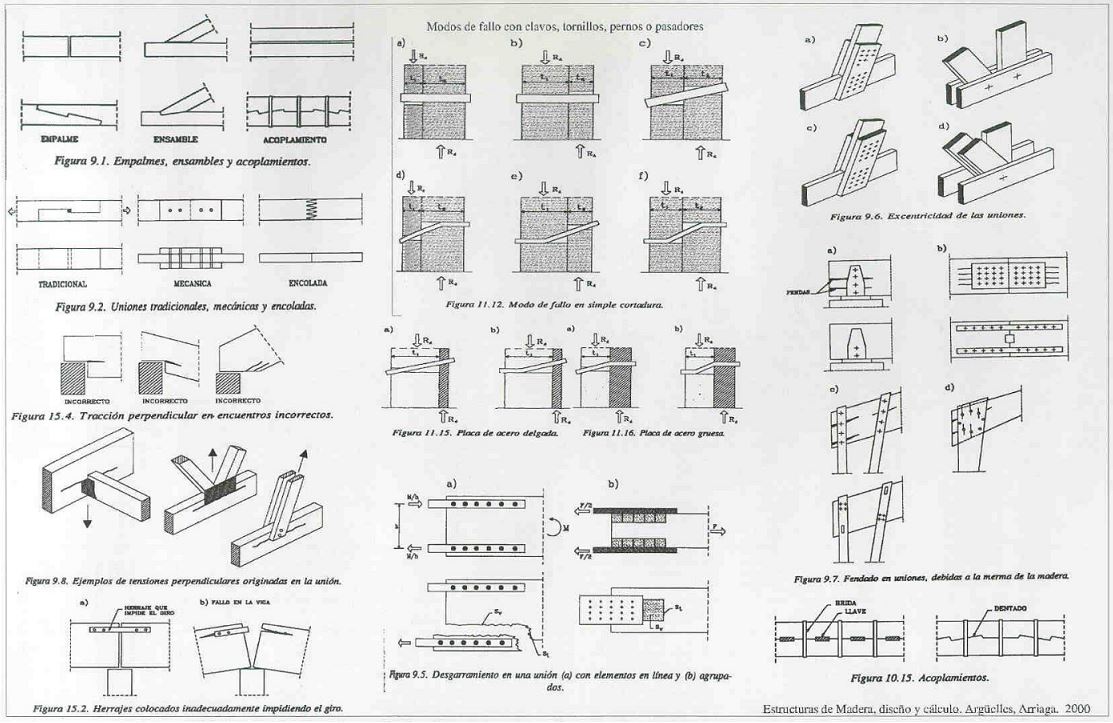
- From the Feim.org (Fonfederación Española de Espresas) They offer us a series of quite interesting manuals on wood as:
- – Basic concepts of wood construction
- – Wood products for construction
- – Behavior in front of the fire
- – Execution, control and maintenance
- – Joints in wood structures.
- – The wooden structure for roofs of houses and rehabilitations.
- – Durability.
- Structural design guide – architecture… in wood HERE
- Wood products for architecture (AiTim in collaboration with the Superior Council of Architects of Spain)… With information HERE
- Thesis. Construction of houses in wood… An efficient alternative?… See HERE.
- From Infomadera we can access to different manuals, guides, videos…etc(From HERE). As an example of some manuals of wooden houses PDF:
- Book Wooden Houses I Generalities
- Book Wooden Houses II Log Houses
- Book Wooden Houses III Heavy Framed Houses
- Book Wooden Houses IV Light-frame houses
- Book Wooden Houses V Half-timbered Houses
- Book Wooden Houses VI Connecting Means
- Book Wooden Houses VII Insulation and Waterproofing
- Book Wooden Houses VIII Structural Calculation
- Book Wooden houses IX Bibliography
- How to choose a log house, by Augusto Cruzado
? Note: The Arup Group has just published a new comprehensive guide on fire safety design in mass timber construction that you can download from HERE.
We only intend to make known the good virtues and types of wood as a material that is acquiring greater prominence in modern architecture for large volume buildings, we hope that the manuals and guides are of benefit.
Frequently asked questions about wood in construction – FAQ
Why is wood used in construction?
Wood is used in construction due to its strength, versatility, sustainability, and relatively low cost. It is a renewable material, easy to work with, and has excellent thermal and acoustic properties. It is used in structures, finishes, furniture, and more.
What types of wood are best for building?
It depends on the intended use, but common options include pine, ideal for structures and furniture; oak, which is strong and durable; cedar, which resists moisture well; and spruce, known for its lightness and strength. Remember that there is a wide variety of woods available on the market.
Is wood strong enough for building houses?
Yes, wood is strong if the appropriate species is chosen and properly treated. Well-designed wooden houses can last for decades, withstand heavy loads, and adapt to different climates. Keep in mind, however, that regular maintenance is necessary to prevent issues like moisture damage and pests.
How is wood protected in construction?
Wood is primarily protected through chemical treatments (to guard against insects and fungi), sealants and varnishes (to resist moisture), fire-retardant paints, and even through structural design—for example, avoiding direct contact with the ground.
Is wood a sustainable building material?
Yes, as long as it comes from responsibly managed forests (certified such as by FSC). Wood is renewable, stores carbon, and requires less energy to process compared to steel or concrete.
What are the advantages of using wood in construction?
Wood stands out as a versatile and sustainable construction material. Advantages include being a renewable resource, offering natural thermal and acoustic insulation, being easy to handle, durable when properly treated, relatively economical, flexible and adaptable structurally, reusable, and available in a wide range of textures and colors.
What are the disadvantages of using wood in construction?
Disadvantages of wood include dimensional changes due to sensitivity to humidity, vulnerability to water and other environmental elements, limitations in size and dimensions, variability in strength and hardness depending on the species, and the fact that it is flammable.
Does wood rot over time?
Yes, wood can rot if exposed constantly to moisture and oxygen (air). To prevent this, various treatments and techniques are used—such as sealants, varnishes, or pressure treatments. However, remember that there are buildings over 100 years old constructed from wood.
Can tall buildings be built using wood?
Yes, thanks to engineered wood products like CLT (cross-laminated timber). There are already buildings up to 24 stories high made primarily of wood, such as Mjøstårnet in Norway.
Why is it important to use sustainable wood?
Using sustainable wood helps preserve forests and reduces the carbon footprint. Sustainable wood comes from responsibly managed forests certified by organizations such as FSC or PEFC.
How can I tell if wood is of good quality for construction?
At a minimum, good-quality construction wood should have a quality certification such as FSC or PEFC, be dry (moisture content <20% for construction), free from large cracks, loose knots, or deformations, and denser woods tend to be stronger.
Is wood resistant to fire?
Wood is not non-flammable, but it behaves predictably in fires. When burned, it forms a layer of char that protects the inner structure and maintains its integrity for a period of time. Fire-retardant treatments can also improve its resistance.
What is the difference between solid wood and laminated wood?
Solid wood is cut directly from the tree, is natural, heavy, and expensive. Laminated wood consists of layers of wood bonded together with adhesives—it is more stable, less prone to deformation, and more affordable.
Can recycled wood be used in construction?
Yes, recycled wood is a sustainable option for finishes or secondary structures. Make sure it is in good condition, without structural damage, and meets local building codes.
How long does a wooden house last?
A well-built and maintained wooden house can last over 100 years. Its longevity depends on the type of wood used, the climate, treatments applied, and regular maintenance.
If you liked the article, rate and share!