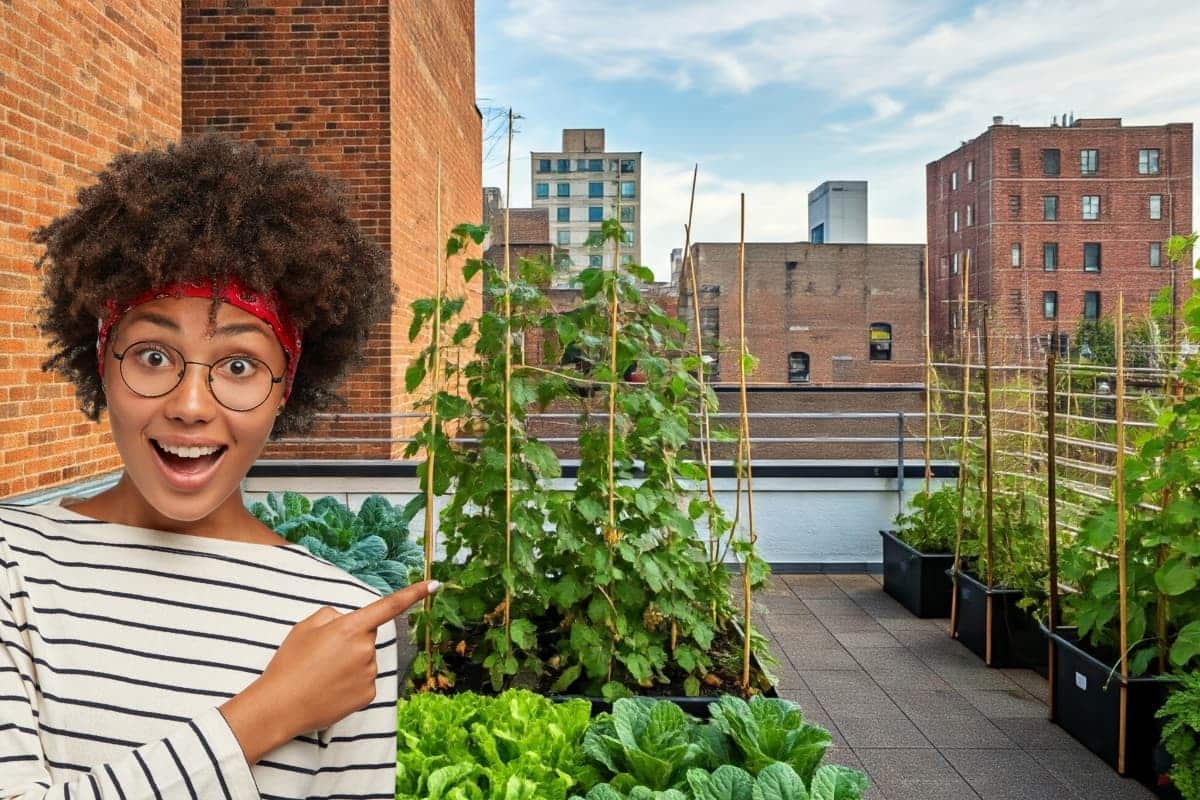
Urban garden
Create your own garden in the yard or terrace, it has many benefits. Especially in food, eating fresh vegetables! It’s already a luxury.
We are what we eat and nowadays we don’t know much about that. Used to comfort, ease, and above all, speed, unfortunately, food is not among our main concerns.
Here is where our urban garden comes in with the intention of producing fresh and quality food. Practice urban agriculture at home!
Urban gardens arise as a response to the search for healthier habits
At the time, we already wrote an article about indoor plants for home decoration. Today, we will learn how to create a home garden step by step with the following guide…
What is an urban garden
An urban garden is an indoor or outdoor space located in urban areas, where edible plants, aromatic herbs, or even flowers are grown. They can be found on rooftops, balconies, patios, community gardens, and even in public spaces.

But… Why set one up? What benefits do home gardens provide?
- We reduce the cost of buying vegetables and herbs.
- Provides access to fresh and organic food, without pesticides or chemicals.
- Teaches us about agriculture, nutrition, and sustainability to children and adults.
- Promotes physical exercise and reduces stress through gardening.
- Fosters a more diverse urban ecosystem and supports pollinators like bees and butterflies.
In truth, it arises from sustainable social movements like slow food or slow life that advocate for the culture of the natural, respecting the time of any process or activity. But…
How to make a home garden
If we want to cultivate a city garden we must follow a series of coherent steps that meet our needs. Let’s see the steps to follow to create a home garden.
First, a good quality summary video to understand urban gardens (Remember that at the end we leave a free course)
In an urban garden, you have to start small, and if we like it, we will invest more money and time!
1.- Location of the home garden
Although it seems obvious, it should be remembered that we have three possibilities for limited spaces; in the gallery – balcony of the house, inside the home (using hydroponic system), and a garden on the terrace or patio, which can be private or community.

Note: In many cities, there are community gardens in suburban areas that are shared and rented monthly, in most cases. In this article, we will focus on a garden built on the building’s terrace with wooden boxes, as it is the most coherent and viable option.
But… What should I look at before deciding where to place the garden? Here are three key elements before deciding the location:
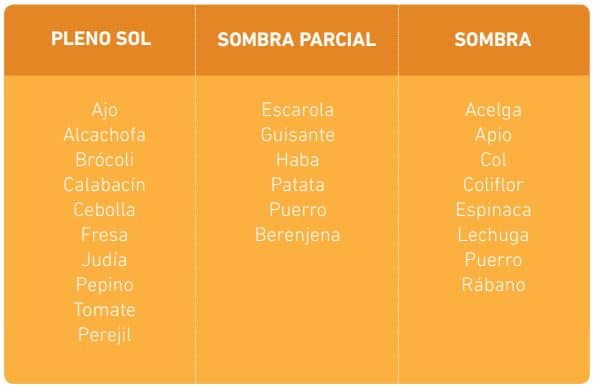
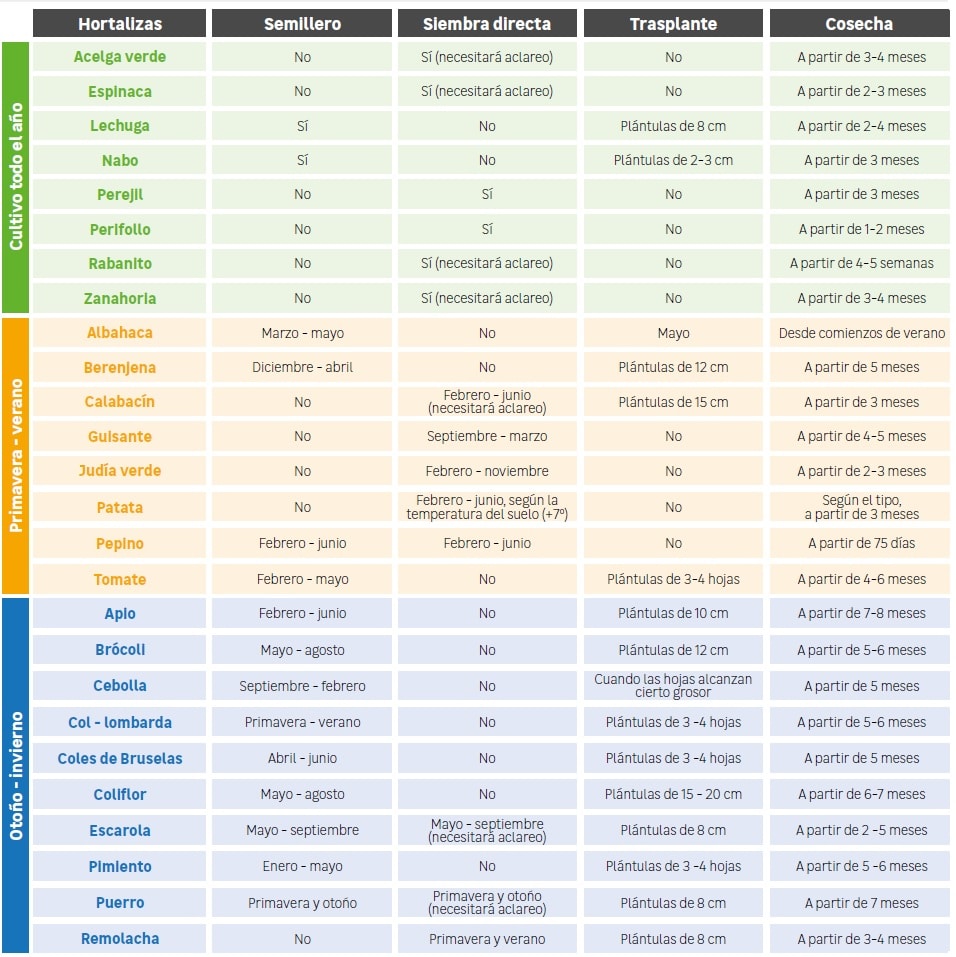
- We need light. We need to find a space with the greatest and continuous exposure to the sun. For vegetables, it should be at least between 5 and 6 hours of direct sunlight a day. In the following table, you will find information on which vegetables tolerate full or partial shade better:
By the way, we have a good article on natural lighting in architecture if you’re interested!
- Orientation matters a lot. For Spain, the ideal is Southwest or South for most vegetables, and for leafy greens (lettuce, watercress, arugula, aromatic herbs, etc.) three or four hours of sun a day are fine.
- Water need. We need to locate the garden in an area where we have access to a water source; either to water or connect the irrigation and drip system.
The best option is to place the garden in the building’s patio or terrace; we don’t take up space at home, it’s located outdoors, we can produce more vegetables for the family garden, we can move well to work coherently, etc.
Remember, if you are going to place a garden on the community terrace, you must ask permission from the community of neighbors.
And if you like designing gardens, there is an article on how garden design changes cities that also has useful design tools.
2.- What tools do I need to work the garden
It depends on the economy and skill of each user. We are going to list the needs and the different tools used to manage a crop on a terrace.

- Lance hoe. Used to remove plant debris and weeds, loosen the soil, aerate. There are ones for children.
- Fork hoe or weeder. Used to dig, loosen the soil, break clods, and weed out bad roots and weeds.
- Cultivator. Used to scratch the surface and aerate it.
- Trowel or transplanter. We can make holes to plant seeds and seedlings.
- Handle rake. Practically used for everything, but with the main function of dragging plant debris.
- Basket and gloves. Baskets are very useful for transplanting and moving soil from one place to another. Protecting our hands is always good, and gloves are the best option for family gardens, make sure they are a bit thick.
3.- What pots can I use in the garden
The market already offers us different types of pots that perfectly adapt to the size of the patio, terrace, or mini balcony. The most common containers we can find for our small garden are:
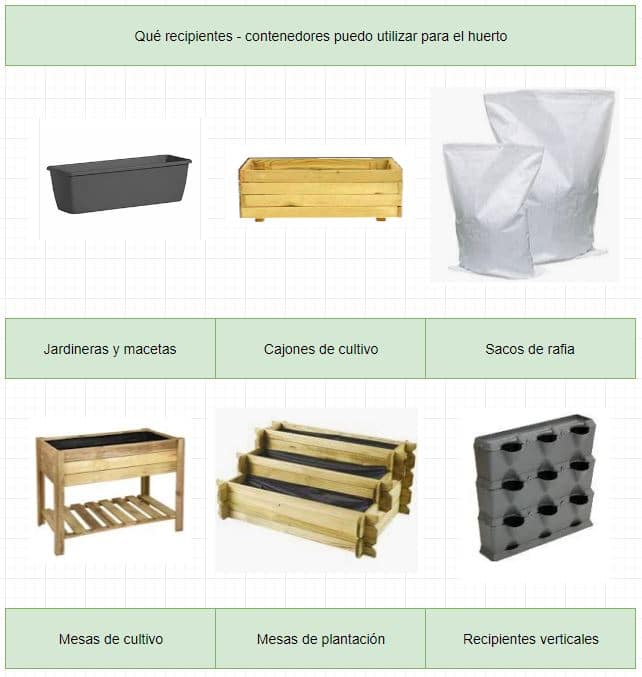
Be careful with the weight of the cultivation tables and sacks on building terraces, we can have serious problems and damage the roof – structure.
Planters and pots
Most planters and pots are already made directly from PVC plastic or bioplastic and come in multiple sizes and shapes, so we have many options to buy. They are the cheapest containers! and we can also make vertical gardens.
Keep in mind that some have a small water reserve tank that supplies irrigation to the plants by capillarity. They are very useful if we are forgetful or go on vacation.
As a counterpoint, in the next article you can see the most original pot we have ever seen.
Growing boxes
They are usually made of wood and treated to withstand outdoor weather conditions. We find them in square or rectangular shapes and different sizes! they are wooden planters!
It has an interior geotextile lining to preserve the wood and contain the soil while maintaining moisture.

The boxes that are a bit more expensive have different compartments that we can use to separate the different crops.
Raffia sacks
Normally people do not usually use raffia sacks for a terrace garden, but it should be noted that sometimes they are very useful because they are lightweight and can be easily transported.
They are also made with a weather-resistant and water-permeable geotextile, and some even have compartments.
Cultivation tables

This is the container par excellence of the urban garden on rooftops. They are easy to handle, small in size, and without water loss.
They are made in different materials such as PVC plastic and wood, with various colors and UV-resistant. Aesthetically, they look very good anywhere.
They usually have an intermediate support to leave cultivation tools and larger cultivation supports, with dividers for the distribution and division of what we are going to cultivate.
The cultivation table is the most used container in urban gardens for its convenience
Planting tables
They are the closest thing to having a small garden. Used in large patios and terraces, and go directly to the ground. Their cultivation capacity is much greater than the previous containers (We will see more later).
They are lined with a protective geotextile, made of wood, and have a protective bottom to avoid dirtying the floor. There are different heights to cultivate low-growing species and others that grow upwards.
Vertical containers
To make the most of small spaces, there are also vertical structures for cultivation where we can create mini-gardens that are installed on walls.
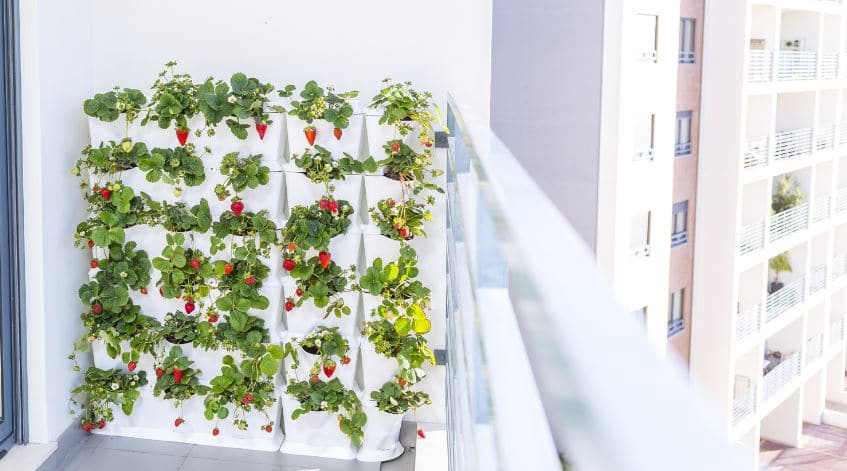

We find them in many shapes that adapt to any type of wall. Very used on balconies or for indoor cultivation in homes to have a mini-garden or the famous “vertical garden”.
They are self-draining and self-supporting modules made of resistant polypropylene material. We have an extensive article on how to buy a vertical garden and what to cultivate.
remember that all containers; planters, pots, boxes, etc., must have a hole for water drainage.
4.- Buy cultivation table
To buy an urban garden, here we play with the sale of the “cultivation kit“, more for beginners where they sell you the complete pack; wooden box, soil with fertilizer, plus aromatic or culinary plants. Or the second option, buy the elements separately which is more for growing vegetables.
First, some tips:
- Pay close attention to the dimensions. Make sure it fits your needs. And if you need the boxes with legs or not.
- If the box is large and you buy it with legs. If you think you will move it over time, buy a metal one with legs (Plastic and wooden ones come without wheels). A box 1.00 meter long weighs more than 100 Kg once filled.
- You can buy a wooden box, plastic, PVC, metal, etc. This is a matter of taste, but wooden ones; besides looking better aesthetically, can be easily painted. Remember, wooden ones, you will have to assemble it, so it’s extra work.
Be careful with the wooden or metal cultivation table! you will have to assemble them! And the big ones, have their work.
- If it is a plastic cultivation table or metal. Check the water tank and drainage system.
- The “weird” wooden structures that lean against the wall, staggered or have a profile for the vine. In the long run, they are a nuisance! we are looking for them to be practical to handle!

We recommend buying the following urban cultivation tables:
- For beginners. You can start with this low wooden box in the style of a urban garden kit from Amazon which is on sale. Suitable dimensions and takes up little space.
- The steel ones with wheels that we like is this one from Leroy Merlin. And on Amazon, they have one that is almost perfect, you can check from HERE this elevated planter! excellent option!
- A high plastic table (robust polypropylene) with legs. We go to Bauhaus from Keter Urban Bloomer because it is very well thought out without being too big, and it is relatively cheap.
- The wooden planters, which are treated for the exterior. We stick with those from Bauhaus, treated with autoclave and includes geotextile that you can check from HERE.
We continue on how to prepare a garden…
5.- What is the suitable substrate for home cultivation
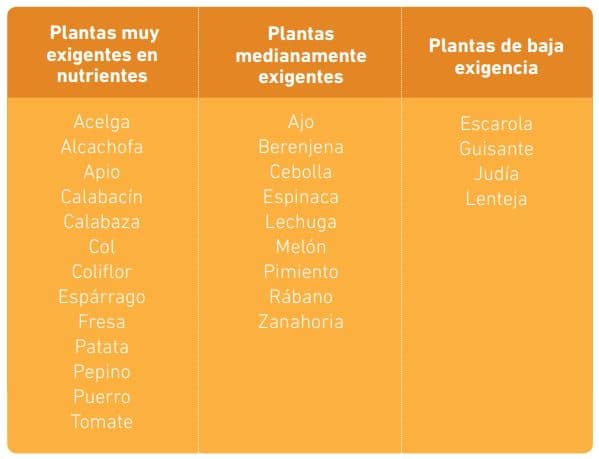
Most fruit trees, aromatic plants, horticultural and condiment plants that we cultivate in the organic garden “are easy to grow” but will need fertile soil, with nutrients, loose and with the ability to retain water. And, in addition, we are practicing urban agriculture.
The suitable substrate will be the one that ensures:
- Support
- Oxygen access to the roots
- Proper moisture retention
- Nutrients

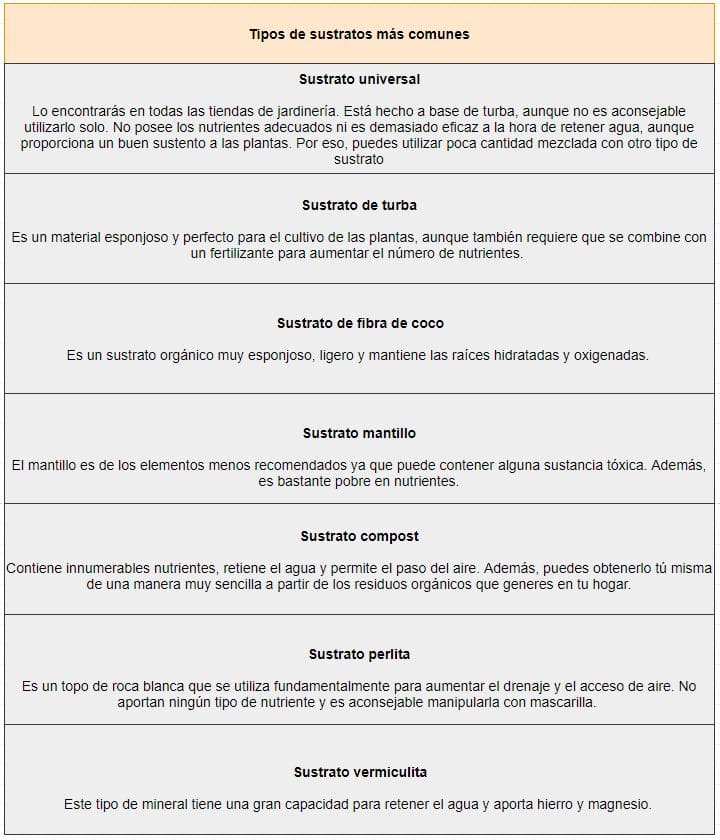
Here, in the first sowing of the garden, we will need the substrate bags that are already prepared and that we can generally find in two types:
- Universal substrate bags. Intended for planting all types of plants with a mix of plant debris, peat, compost, and NPK fertilizer (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium).
- Specific substrate bags. There are substrate bags specifically for the garden ensuring nutrients in the first weeks thanks to a higher content of fertilizer – guano. (Peat substrates, coconut fiber, mulch, compost, etc.)
Every time you finish a cultivation cycle and remove the plants, it is advisable to
stir the substrate. And every two years, change everything.
Remember, the success of our ecological garden not only depends on the substrate, but also on environmental conditions, the choice of varieties we use, or the cultivation season.
A good substrate will guarantee the supply of nutrients without having to think about it for a long time.
Highly recommended! Ask in a specialized store what substrate we need for the garden according to the “X” vegetables and plants we are going to plant.
And how to choose a good substrate from the following video gives us the keys…
If you are determined to make a combination yourself and are a purebred urban farmer. The best option is to combine several of them. To start…
- 40% coconut fiber
- 20% universal substrate
- 15% compost
- 15% fertilizer
- 10% vermiculite
The fewer chemical fertilizers, the better, we must take advantage of the waste generated at home. Organic and free fertilizer! We can make them at home with the help of a composter kit.

You can learn more with the good composter manual from HERE, very useful the diagrams at the end of the PDF.
It benefits us all, it is about taking care of the environment and at the same time, transforming waste by recycling it to make good use of it.
In the end, it is about complementing cultivation techniques, being able to turn waste into humus, to help fertilize the substrate.
6.- How to prepare the cultivation bed in the container and sowing
Before starting to cultivate, make sure that the containers you use; planters, pots, boxes, etc., have a hole for water drainage. And now, follow the steps in the following diagram:

7.- What can I plant in an urban garden
First, in home gardens, we must know that we have two options for seedbeds in nurseries for our outdoor plants to grow. We can buy seed packets or seedlings:
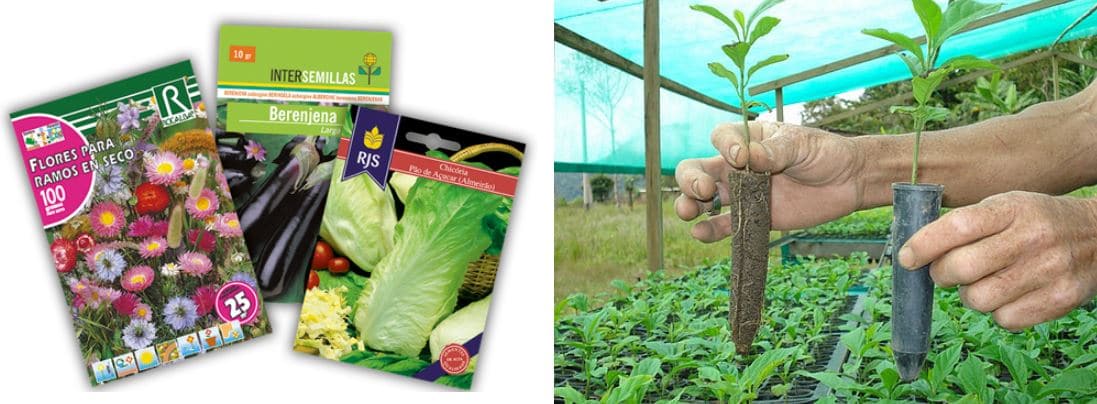

Buy seeds in packets. For our ecological gardens of small dimensions, the seeds will be planted directly in the soil without creating seedlings in a specific seedbed. Always see instructions on the packet.

Although if we have a seedbed to create seedlings we can control more and better the germination and obtain seedlings at home.
To start, we will practice direct sowing with the following tips:
- When we make the hole for the seed it should be at least three times the size of the seed.
- Large seeds are sown in groups (in groups of two or three)
- Small seeds are sown by broadcasting (throwing handfuls over the substrate)
- To facilitate germination and protect them from the wind it is advisable to tamp the soil a little with the palm of the hand after sowing.
Buy seedlings. The seedlings are seeds that have grown for “X” time. As we have mentioned, we can make them at home or buy them directly in a nursery.

When you plant them, take into account the distance between the different seedlings so that they grow properly.
What to sow in an urban garden? Almost all species are suitable for cultivation in an ecological garden, however, the most recommended are:
| Lettuce | Tomato | Green bean | Strawberries | Zucchini |
| Eggplants | Peppers | Potatoes | Carrots | Radishes |
Throughout the year you can have fresh vegetables if you know when is the right time to sow and for that, there are sowing calendars.
As a guideline for urban cultivation, we leave an excellent calendar (Spring, summer, autumn, winter) that indicates the tasks: sowing, transplanting, and harvesting, but you should always check the instructions on the seed packets.
Aromatic plants (basil, thyme, oregano, rosemary, parsley, etc.) are ideal for planting in pots, and are indispensable in any kitchen. Due to their intense aroma, they repel insects that attack plants more frequently. They do not require much care and grow easily.
Remember, first garden, simple crops!
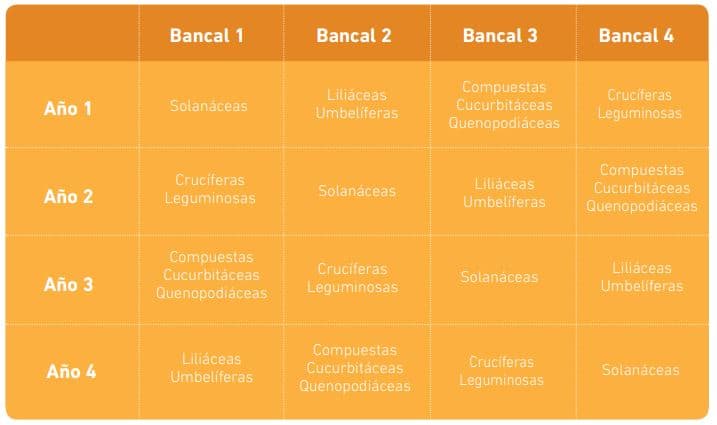
The rotation of crops is important. Apart from the distances we must keep between plants, it is advisable to know that not all varieties of vegetables can be grown next to each other.
In home gardens with pots and boxes, we can follow the rotation by marking each pot with a number to serve as a guide. In crop rotation methods. One of the most common is the botanical family method:
- Sowing 1: Solanaceae (eggplants, peppers, and tomatoes).
- Sowing 2: Liliaceae (garlic, onions, and leeks) and Umbelliferae (celery, parsley, and carrot).
- Sowing 3: Compositae (lettuce and endive), Cucurbitaceae (pumpkins, zucchini, melons, watermelons), Chenopodiaceae (chard and spinach).
- Sowing 4: Cruciferae (broccoli, cabbages, and cauliflowers, radishes)
and legumes (beans, peas, and chickpeas).
Since we all have mobile phones, there are mobile apps for the garden and gardening that will come in handy. Two stand out above the rest:
- The app My Garden: Crop Management from HERE. It is possible to investigate a vegetable or fruit to know when is the right time to carry out your gardening work using the influence of the moon, which is called biodynamics.
In the following YouTube playlist we can learn how to plant the following vegetables in detail.
| How to sow in the garden: | |||
| lettuces | chard | cabbage | cucumbers |
| broad beans | tomatoes | peppers | zucchini |
| eggplants | beans | peas | carrots |
| radishes | onions | potatoes | |
8.- Fertilizers for gardens
Nowadays, in stores, we can already find specific fertilizers for gardens with specific crops.
The primary function of these fertilizers is to have an abundant and quality harvest in addition to intensifying the flavor. Most are organic-based, guaranteeing organic farming due to their formulation.
There are mainly three types of fertilizers for the urban garden:

- Composted fertilizers. It is mulch, horse manure, worm humus, or homemade compost. A thin layer is usually spread over the substrate or by digging a little.
- Granulated fertilizers. These are fertilizers that are distributed around the plant and slowly dissolve with irrigation water so that the nutrients can be absorbed by the plant roots.
- Liquid fertilizers. This type of fertilizer is dissolved in irrigation water and is very practical. They are fast-acting fertilizers.
Also, in the market, we have inorganic or chemical fertilizers, and although they are not usually used in small gardens, we will find them in granulated or liquid format.
To apply fertilizer in the garden, read the manufacturer’s instructions
But… How often should I fertilize? First, we have to read the manufacturer’s instructions and, as a general rule, fertilizers are applied with a frequency ranging from a month to a year depending on the soil’s richness, the type of crop, or the fertilizer you use.
9.- How to water the urban crop
In city agriculture, the plants and vegetables grown in a container need more water than those living in the ground.
Tips for watering garden plants:
- Watering is done frequently and briefly, but in smaller amounts to avoid waterlogging.
- Do not water under pressure. Use watering cans with a rose to let the water fall gently.
- Depending on the type of plant, the frequency and duration should be adjusted, as well as the development stage, the time of year, and weather due to planting density.
- The watering schedule changes according to the season; in summer, it is done in the early morning or when the sun has set, and in winter, autumn, and spring, in the central hours of the day.
- All containers must have a hole to drain to avoid accumulation.
- It is good to avoid wetting flowers, fruits, and leaves to prevent the appearance of fungi.
group the vegetables according to the water they require so that all receive the appropriate amount
If we are not satisfied with the typical hose or watering can for watering and want a more complete drip system for the urban garden, we can set up an automatic irrigation system for the terrace.
The models of automatic irrigation already represent a greater investment and budget, although they provide better water use and less constancy.
Due to its complexity, knowledge or professional advice is needed, broadly speaking, we leave a diagram of an automatic irrigation installation for a terrace with different scenarios:
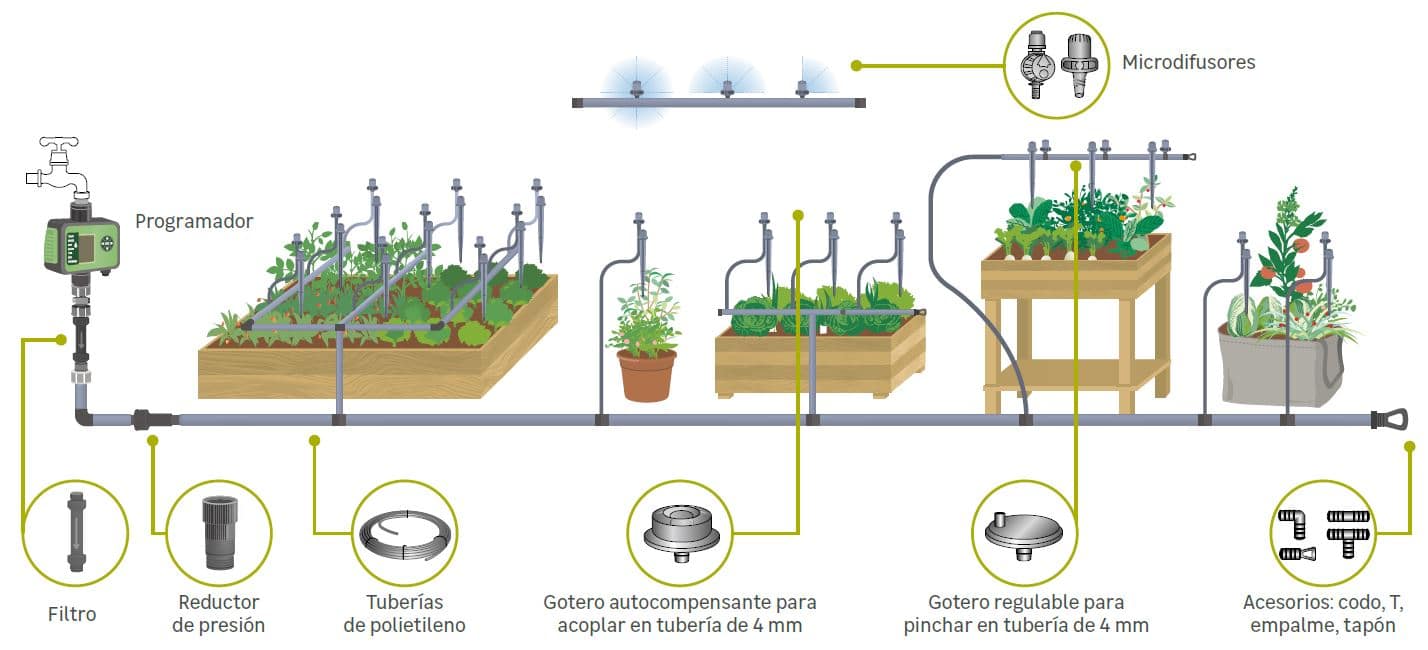
To learn more about how to install an automatic irrigation system for pots, we leave the following video…
Pests in the garden
This is a complicated topic and in some cases, we will need a professional to eradicate a specific pest or disease we have in the garden.
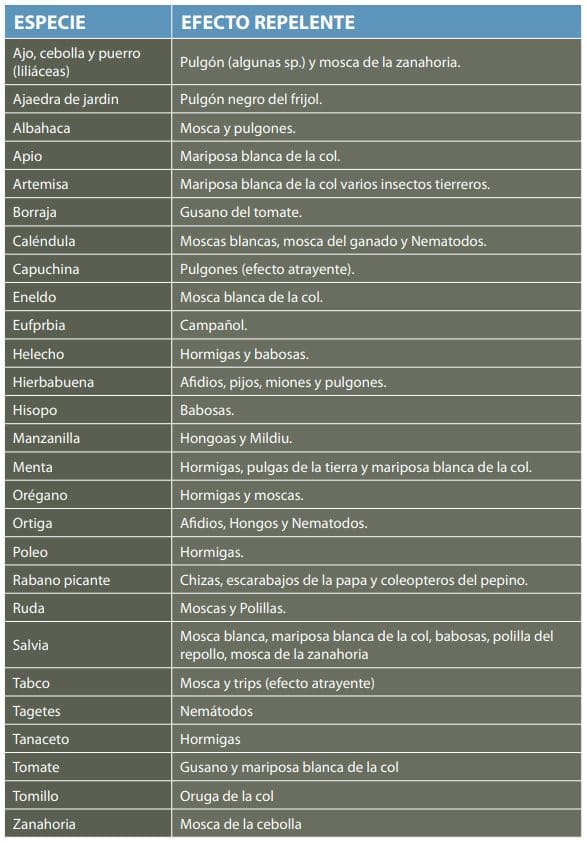
As a diagram, we leave the following infographic on common pests in gardens and what live plants we can use as repellents:
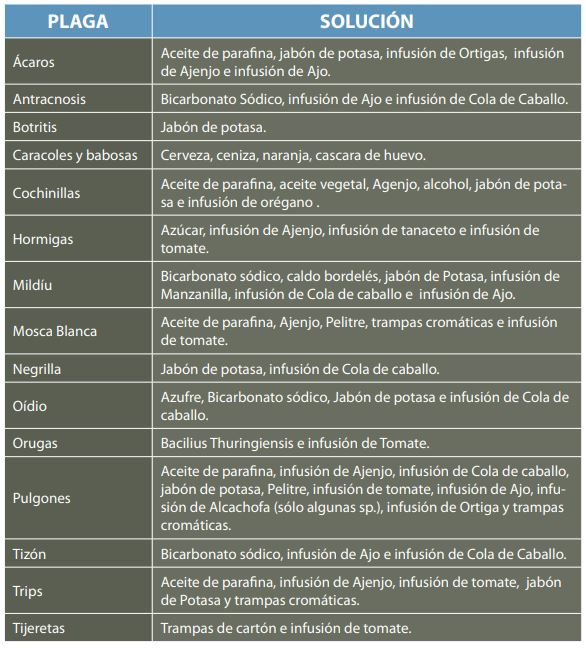
If we want to use ecological remedies for garden pests, we can see the following infographic on pests and their solution:
Online course to set up a small garden
I think if you are interested in the topic you should watch the four YouTube videos of a small online course that you can watch from HERE. It covers the topics of:
- Lesson 1: Select the crops that best suit you
- Lesson 2: How to sow and transplant
- Lesson 3: How to water and fertilize well
- Lesson 4: Pest treatment
Remember some tips:
- Among the most practical products to plant at home are tomatoes, peppers, onions, chamomile, or parsley. If we want, it will even be easy to make an organic garden at home if we use organic fertilizers.
- Spring is a good time for the cultivation of these products as there are no frosts at night.
- Watering should be adjusted to the time of year, climate, and the number of plants. Thus, while in winter we will only need to water them once or twice a week, in summer we will have to do it more frequently.
- Be careful with the light, it can ruin our garden. The best orientation is to the south, where the plants will get the light and heat necessary for good growth.
- Regarding fertilizer and fertilization, it will depend on the plants. Those from which the fruit is eaten, such as tomatoes, peppers, or eggplants, need more than onions or lettuces. It is usually done two or three times a year, without changing the content of the tub and only adding the necessary nutrients.
- The advantage of cultivating in such a small space is that the possibility of pests appearing is lower. The most common are aphids and whiteflies, which are eliminated by spraying soapy water. For the red spider, the best thing is to place onion skins around the plant to act as a repellent.
- With all this, we will enjoy the smells, flavors, and textures of the rural world in our home.
What are the benefits of an urban garden

- In the home garden, we produce our own food and know what we are eating with our home gardens.
- We rediscover the aromas and flavors of vegetables and fruits.
- If we have a home garden, we improve our diet by eating healthier.
- We do not contribute to the increase of intensive agriculture and genetically modified foods.
- We improve the biodiversity of the city and air quality (although on a small scale, it is our contribution to the sustainability of cities).
- We improve our relationship with nature (we know the natural cycles of the earth and the biological cycles of vegetables, their properties, we increase our knowledge of the natural environment, etc.).
- It provides benefits to our mental health (it is an excellent stress reliever) and a fun, relaxing, and healthy activity.
- If they are community gardens on building terraces, we improve coexistence with neighbors.
Of course, not everything is an advantage when you decide to grow your own food, and to be honest, practically the most notable disadvantage of having a mini garden in the home is that you have to take care of the budget you allocate – especially at the beginning – and that it must be a long-term project.
Documents of interest if we want to learn more:
- How to make an urban garden – From Intermón OXFAM
- The urban garden guide – From Leroy Merlin
- Complete cultivation guide – All about the garden from YouTube
- Urban garden initiation manual – From Bauhaus produced by Concept Agency
- Guide for starting and maintaining home gardens – From Incorpora Formación.
- Manual of sustainable home gardens. Via Alicante Natura
If you liked the article, rate and share!