Internet of Things IoT
Whether we like it or not, the reality is that we are moving towards a way of understanding life that is totally “connected” with many digital devices and technology, and this will affect the way we understand cities and how we inhabit them, among many other aspects.
And here is where the example of Internet of Things (Internet of Things – IoT) comes in…. Do you think that an orchid will be able to tell its story? Do you think it is possible to teach a building to speak or change color according to the weather outside? Do you think a car can call an ambulance faster than a phone?
What is the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things, known as IoT or Internet of Everything in English, is a network of smart physical devices connected to the internet, collecting and sharing data in real-time, creating a dynamic digital ecosystem.

The IoT technology must be able to communicate with each other, have control over objects, detect their environment, and make decisions based on specific needs to help us in our daily lives.
The true value of the Internet of Things does not lie in the devices, but in the data they generate and how we use them
How the Internet of Things works
The IoT works through a network of smart devices with sensors, software, internet, etc., called “things”. These capture data from the environment; for example, temperature, humidity, movement, etc., and send it to an online cloud platform for analysis.
The operation of the IoT is based on the interaction of three key elements:
- IoT Devices: These are physical objects equipped with sensors, microcontrollers, and internet connectivity. These devices can range from simple temperature sensors to complex industrial robots.
- Connectivity: IoT devices connect to the internet through various wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE, etc.
- IoT Platform: This is the platform that centralizes the collection, storage, and analysis of data generated by IoT devices. This platform allows data visualization, alert generation, task automation, or application development.
? Note: This concept originates from an advanced science and technology work published in 1999, When Things Start to Think, by researcher Neil Gershenfeld from MIT. He wrote… “Besides trying to make computers ubiquitous, we should try to make them unobtrusive”.
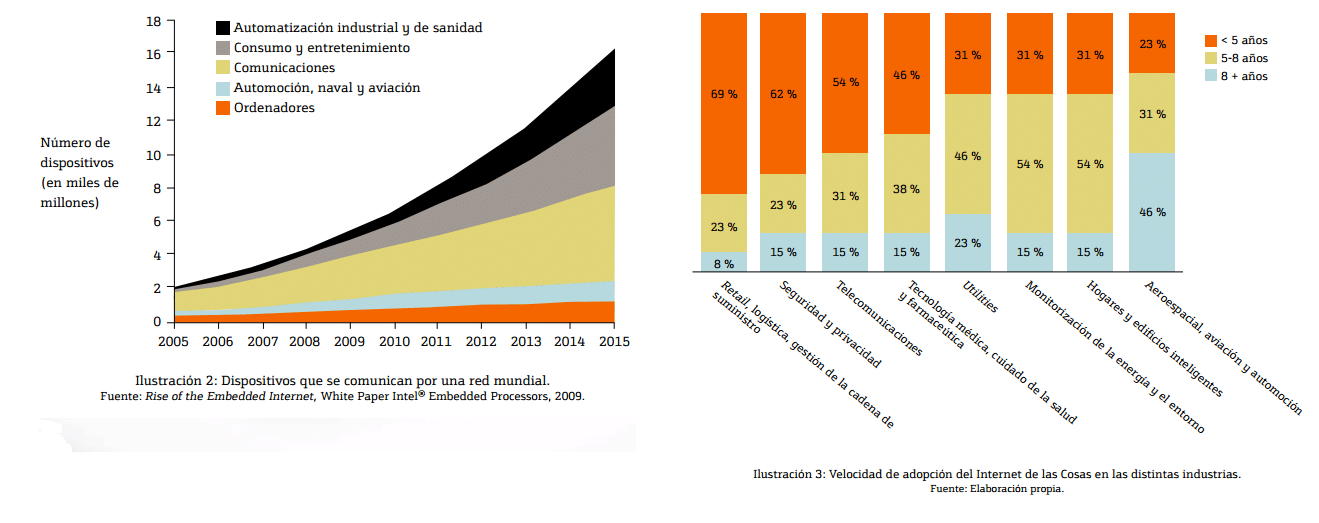
These aspects are revolutionizing different sectors of the internet industry, including the way we inhabit and understand buildings, homes, or transportation. In the following graphs, we can identify the evolution it is having and the speed of adoption by sectors… How smart are things today?
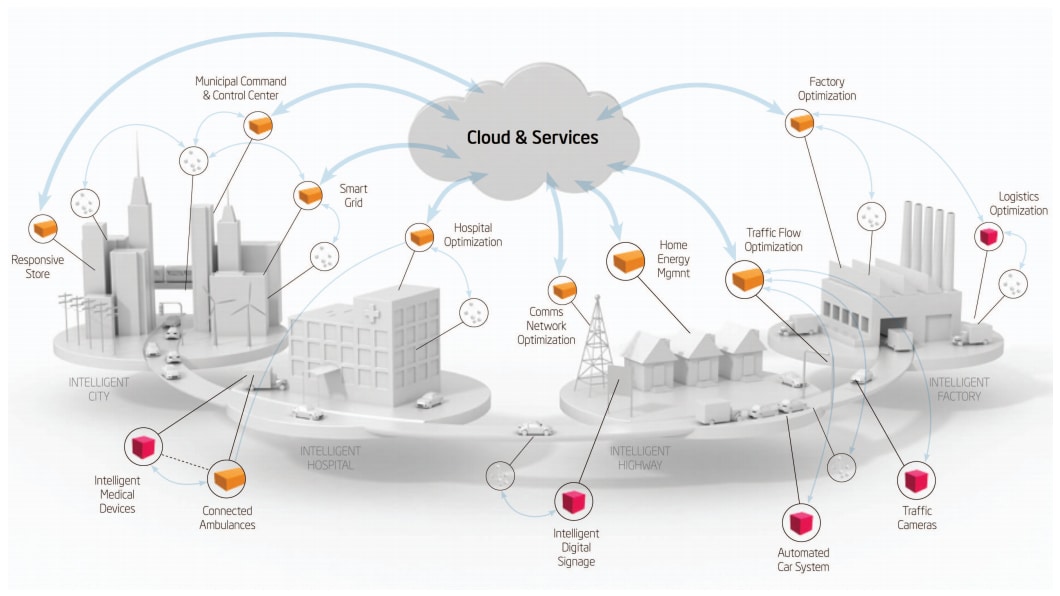
A revolution of the Internet where everything is connected to the network. “The Internet of Things is not just a trend, it is a revolution that is changing the way we live, work, and interact with the world.” – Marc Benioff, CEO of Salesforce.
So… What are the benefits of the Internet of Things?
- Greater efficiency and productivity: it automates repetitive tasks and optimizes processes, freeing up time and resources for more creative and strategic activities.
- Improved decision-making: The analysis of data generated by IoT devices provides valuable information for making more informed and strategic decisions.
- Cost reduction: It optimizes resource use, reduces waste, and minimizes operational costs.
- New business models: It opens the door to new business opportunities and innovative service models.
- Greater comfort and quality of life: It facilitates daily life and improves quality of life in various aspects.
Although we always think it is a trend for the home, in truth, it encompasses almost any sector… And in construction?
How the Internet of Things affects construction
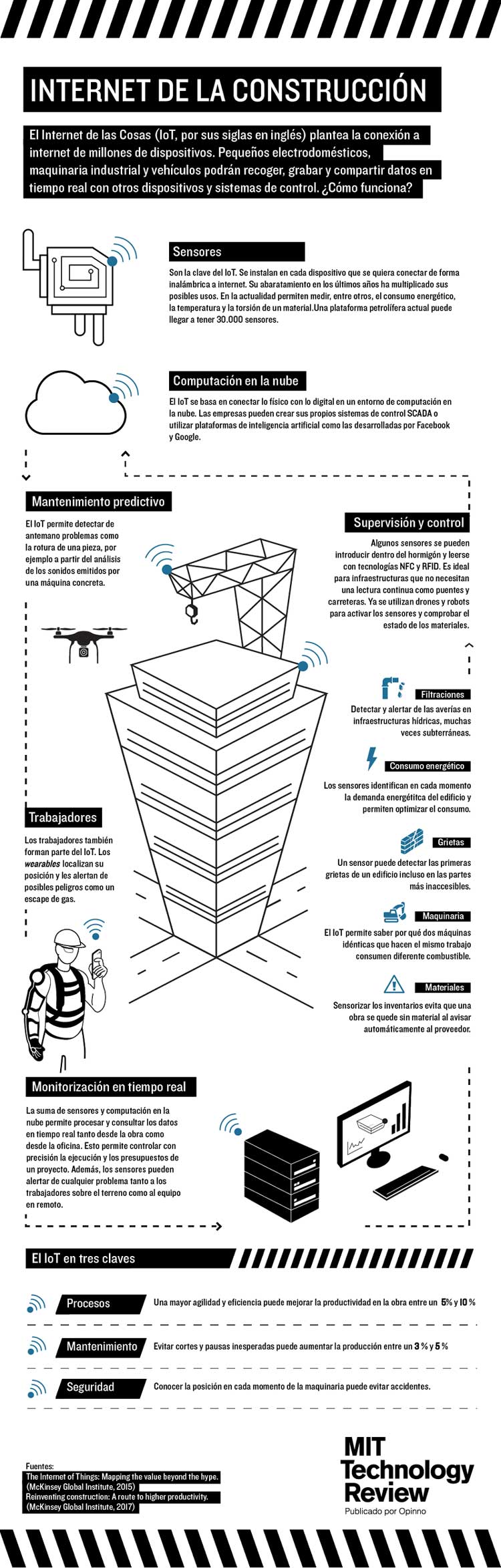
Construction sites and buildings are beginning to feel the technological pulse that brings new control capabilities, real-time data, and resource efficiency to projects. From MIT, they provide us with one of the most interesting infographics to recognize the most relevant aspects of utility:
? Note: We can see the article on current most innovative technologies or the new generation materials, you will be surprised at how the world is advancing.
How it affects housing
In the following video, we can test an example of how an ordinary day will be where technology is fully integrated into our daily lives with IoT:
Evidently, the term IoT goes beyond architecture or interior design of houses, represented in a word we all already know, the Smart Cities.
These futuristic and smart cities that “theoretically” will provide us with a more pleasant life through different mega-connected systems, an improved habitat, more security, environmental sustainability, where the energy efficiency of things will be enhanced to its fullest expression and, which are currently so fashionable.
We recall the article The future of Smart Cities and their investment where we confirmed that the growth prospects for 2025 of smart cities or Smart City are four times more. But…
How it affects cities
Cilab’s Smart City is an advertising video about how Internet of Things technologies can make our cities smarter and minimize the environmental impact of our daily activities.
We can already identify that the new capabilities of Internet over objects move a lot of money. In the article from Eleconomista…“ It will mean global savings of 14.5 trillion euros. European trillions. Eleven of them correspond to the private sector and the rest to the public. Because it would translate into more efficient asset management (including energy management in smart buildings) and productivity improvements”.
The Internet of Things turns cities into smart environments, improving urban efficiency and sustainability.
Although we can verify that it can undoubtedly bring benefits to society or individually, there is always a but, some advantages and disadvantages of the Internet of Things that we want to show. Without entering into the discussion of… Who is behind? Looking at the big electronics companies and their multiple “hidden” interests.
Advantages of the Internet of Things
- Increase in a new business model and opportunity. New services that better respond to the specific needs of citizens.
- The technology of things will allow the detection and capture of different events, providing detailed and real-time visibility of what is happening in a building, of possible actions that can be taken according to climate changes…. etc. Reduction of expenses that a property can produce, electricity, community…etc. In short, a greater adoption of the efficiency of the resources available to a building.
- Time savings for the user, both individually and in the community.
- Automatic and efficient management of urban infrastructures. Improved energy savings, improvements in energy efficiency …etc. Improvement in the management of urban mobility and parking, to improve traffic and reduce search times for parking spaces, reduction of queues and waiting times in municipal offices and health centers, etc.
- Improvement of urban planning and environment. Detection of deficient or to be improved infrastructures. More efficient green areas with less resource expenditure. More controlled peripheral areas…etc.
Disadvantages of the Internet of Things
- Funding by the Administration or the individual, as a significant investment in technology is required.
- Given the implementation of a high degree of technology, there is a dependence on companies that offer these services. Both at the public and private level.
- Reduction of privacy. “To be more efficient, it must be observed what habits the consumer has in all aspects and levels”
- Properties become more expensive. They are more complex to execute and build.
- Greater technological gaps between cities and realities. Not all cities can afford such a cost, so first-class and second-class cities, buildings, or neighborhoods will appear.
- Due to the complexity that the Internet of Things absorbs, they simultaneously produce a considerable increase in waste.
Key factors of evolution and challenges
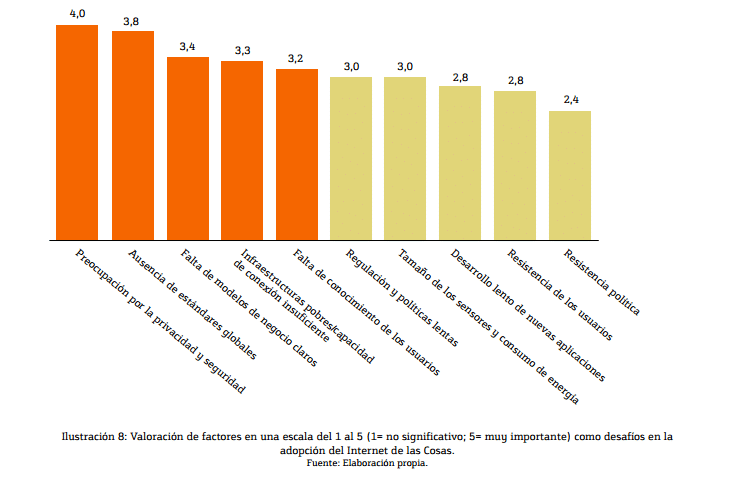
We are clear that the evolution of the Internet of Things is unstoppable and that to a large extent, it brings benefits to society.
But there are also certain reticences in its implementation, especially when we talk from the perspective of large companies, whose main objective is to benefit from that information to increase their revenues.
Examples of Internet of Things
Examples of IOTS or the famous Internet of Things we can find many and more, if we delve into the different “gadgets” and systems that flood the technology market every day; from mobile apps to measure anything or notify us, smart objects that talk and think, to the latest vacuum cleaner that knows when our house is dirty.
The applications of IoT that we can quickly identify are:
- Smart homes: Devices can automate household tasks; turn on lights, adjust temperature, control appliances, etc.
- Smart cities: It is to improve city management, optimizing traffic, lighting, etc.
- Industry 4.0: For real-time monitoring of machinery and processes, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Precision agriculture: Monitoring factors such as soil moisture, temperature, or even plant health.
- Connected health: Monitoring people’s health to provide data to medical professionals for better diagnosis and treatment.
Pointed out examples, for instance, the following smart “stickers” that are added to objects to provide data about them, we just have to program (they are already defined easily) what we want them to communicate to us.
An example, it is added to a pot and will tell us when was the last time we watered it or, depending on the temperature where it is located, if it needs more or less water…

An example of smart technology is a sensor for the garden. The device records data on temperature, sunlight, humidity, or fertilizer level in the soil.

To have a greater global perspective and understanding, we add as an example of Internet of Things the following video. Openarch is a real prototype of a smart home, a project by Sori.
The first home designed from the start to incorporate a digital layer that connects the house and its elements to the Internet. It represents the sum of many small applications of new technologies in the home, using devices like Kinect, webcams, projectors with multiple sensors to measure from CO2 to electrical consumption.
To learn more: Publications on IoT
- Fundación Bankinter (The internet in things in a world connected to smart objects in Spain)… from HERE.
- Industrial Internet Insights for 2015 (General Electric and Accenture – The report, based on a survey of executives, indicates that executives in the industrial and healthcare sectors see enormous potential in the Industrial Internet, the combination of big data analytics with IoT technology)
- Opinion 8/2014 on the on Recent Developments on the Internet of Things (European Commission – The report is the first joint opinion on the Internet of Things approved by European data protection authorities. It identifies the main data protection risks arising in the Internet of Things ecosystem and provides guidance on how the EU legal framework can be applied in this context)
- 2014 State of the Internet of Things (Accenture Interactive – The report is based on a survey of over 2,000 US consumers and examines their adoption of connected devices and smart technology now and in the future)
Now an evolution (revolution, as many say) is approaching that is based on the connection of all kinds of devices, including many that we often do not believe can be connected… In the following TED talk, it explains the future of this trend.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Internet of Things – FAQ
- What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the concept of connecting everyday devices to the internet, allowing them to collect and share data with each other. Examples include smart appliances, wearables like smartwatches, industrial sensors, and connected security systems.
- What is the Internet of IoT?
It is the English abbreviation for “Internet of Everything,” which is often referred to in Spanish as the Internet of Things.
- How does the Internet of Things work?
IoT works through a network of smart devices equipped with sensors, software, internet connectivity, etc., known as “things.” These devices capture environmental data—such as temperature, humidity, or motion—and send it to an online cloud platform for analysis.
- What devices are part of the IoT?
Almost any device can be part of the IoT if it has internet connectivity. Examples can be found in smart homes (lights, thermostats, locks, and security cameras), healthcare (smartwatches, fitness trackers), smart cities (traffic lights, traffic sensors, connected garbage bins), or industry (robots, machines, and sensors in factories).
- What are the benefits of IoT?
IoT offers many benefits such as task automation, increased energy efficiency, health improvements, industrial optimization, cost reduction, and more.
- What are the risks of IoT?
Some risks of the Internet of Things include collecting too much personal information, data security concerns due to potential hacking, and technological dependency, where network or device failures could cause significant issues.
- How big is the IoT market?
The IoT market is growing rapidly. It is estimated that by 2030 there will be more than 25 billion connected devices worldwide. This includes applications in homes, cities, industries, and vehicles.
- What is the difference between IoT and AI?
IoT focuses on connecting devices and collecting data, while AI focuses on analyzing that data and making intelligent decisions. In other words, IoT provides the “eyes and ears” of a system, while AI acts as the “brain” that interprets the information.
- What is a smart home?
A smart home uses IoT devices to automate and control aspects such as lighting, temperature, security, and appliances. For example, you can use your phone to turn off the lights or adjust the thermostat when you’re not at home.
- What is a smart city?
A smart city uses IoT technology to improve the quality of life of its residents. Examples include efficient transportation systems, sensors to monitor pollution, smart street lighting, and optimized waste management.
- What impact does IoT have on the environment?
IoT can have both positive and negative effects on the environment. Positive: greater energy efficiency and reduced waste. Negative: the manufacturing and disposal of electronic devices can increase pollution.