Cellular concrete
Lately, there is talk in the architecture sector about cellular concrete, also known as aerated concrete, for the construction of houses.
At this point, there are opinions for all tastes! Some consider it an excellent system of sustainable construction, others debate whether it is economically viable due to the cost of cellular concrete blocks, and so on all day.

Do you want to learn about this construction material? We explain everything in detail…
What is cellular concrete
Cellular concrete is a porous and lightweight construction material that is manufactured by mixing mainly cement, lime, silica sand, water, and a special foaming agent that creates that alveolar structure.
The mass of lightweight concrete has small and uniform air bubbles – porosity – that provide construction and insulating advantages over ceramic bricks or traditional blocks.
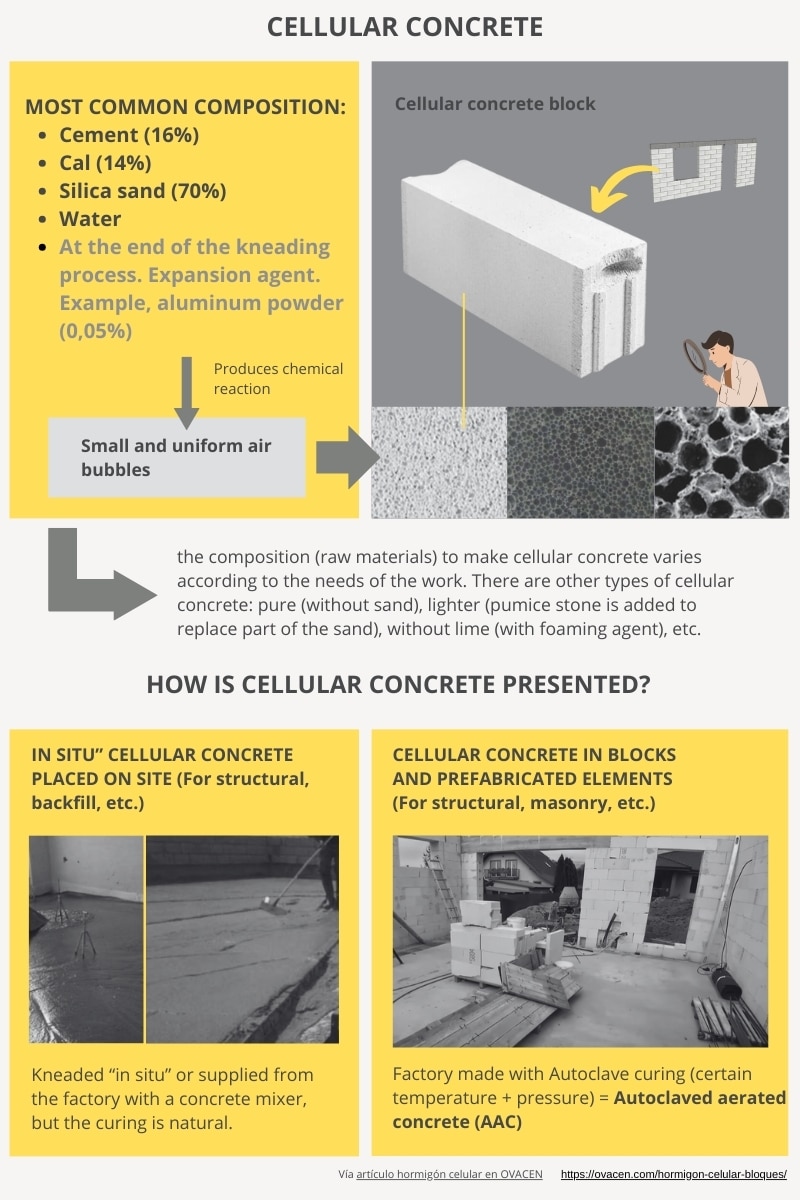
Like printed concrete or pavement, it can be created “in situ” for certain situations or purchased as prefabricated elements and blocks (Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC)) mainly for masonry.
So… What characteristics does this highly insulating construction material have?
Characteristics of cellular concrete
The porosity of cellular concrete provides unique properties that make it ideal for construction, works, or rehabilitation. From a technical perspective, we can see the following image according to lightweight block thickness:
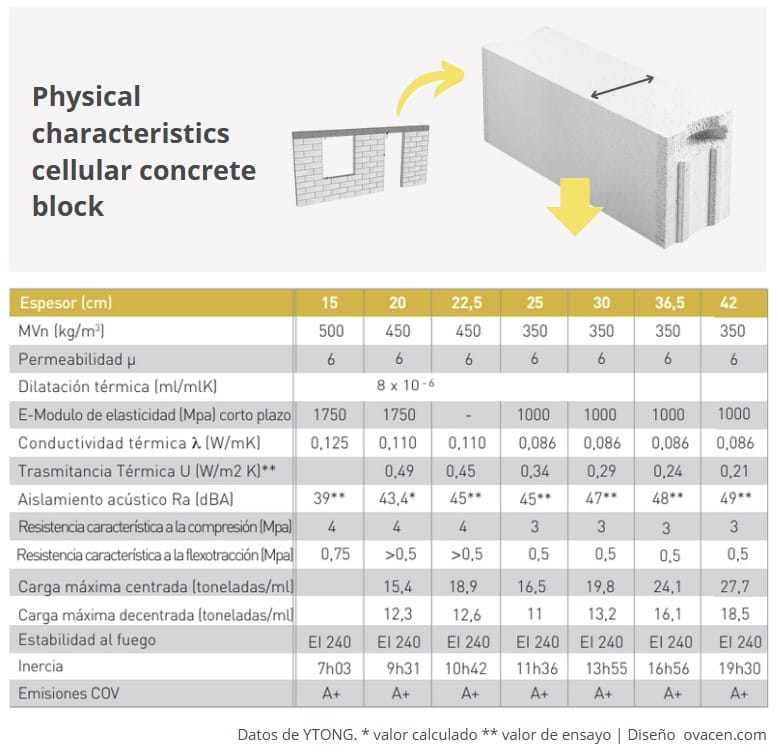
Where aerated concrete blocks really stand out is in insulation, high energy efficiency, far superior to conventional ceramic brick and concrete block pieces
The most notable characteristics are:
- It has an excellent behavior in thermal and acoustic insulation due to its alveolar structure with tiny air bubbles.
- Lightweight, with low density and high porosity, much lower than other traditional materials like ceramic bricks or concrete blocks.
- There are all kinds of prefabricated pieces for the execution of a house.
- It can be used “in situ”. It is pumpable and self-leveling, with a consistency that can vary from plastic to fluid.
- Resistance with structural capacity, load-bearing wall. Especially if we talk about prefabricated due to its homogeneity (Autoclaved Aerated Cellular Concrete – AACC) and of a certain width. Watch out! It is not reinforced concrete.
- Non-combustible, fire-resistant.
- It has a high water vapor permeability.
- Pigmentable, allows a variety of colors.
- Cellular bricks and prefabricated elements can be easily cut, even with a carbide saw.
A cellular concrete block has less density than water, that is… the brick floats in water!
When is it advisable to use cellular concrete?
The use of aerated concrete is very varied in the construction sector: for masonry of constructions, industrial buildings, as thermal insulating material for roofs, walls, or floors, in rehabilitation, sidewalks, etc.
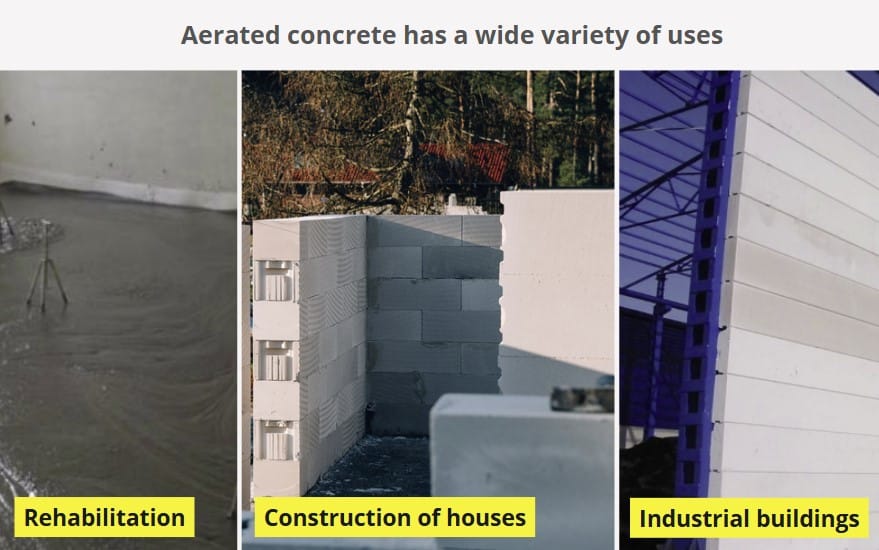
The versatility of lightweight concrete pieces is enormous, they can even be used as a structural element!
| Common uses of cellular concrete pieces | ||
|---|---|---|
| Interior and exterior insulation | Insulation of roofs, garages, or basements | Roof insulation |
| Exterior enclosure with load-bearing capacity | Interior separation | Thermal bridge solution |
| Roofs and slabs | Sectorizations, elevator shafts | Partitions and linings |
| Drywall partitions | Chimney duct lining | Thermal separations |
| Fire sectorizations | Elevators and installation shafts | Passivation of metal structures |
Even factory pieces can be used as structural elements; for slabs, roofs, or in load-bearing walls based on cellular block. In the case of house construction:
- Cold climates: It is excellent for regions with low temperatures, where materials with thermal properties are needed to prevent heat loss from the building.
- Hot climates: It also acts effectively by preventing heat from entering the building.
- Temperate or extreme climates: It works well in areas with extreme temperature variations, both in winter and summer, providing good thermal insulation in all seasons.
What type of prefabricated cellular concrete pieces are there?
The large companies that market cellular have a huge catalog of pieces – including specialized tools – for the construction of a house. An example:
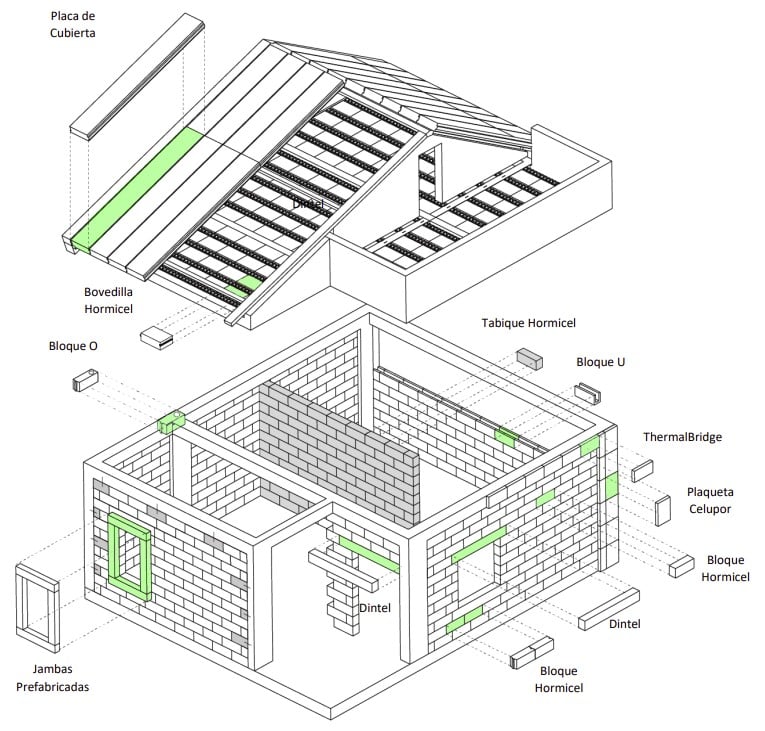
The main pieces made with autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) are:
- All types of blocks/bricks for construction (Both for exterior and interior)
- Lintels (Reinforced, unreinforced, U-shaped)
- Jambs
- Vertical beams
- Horizontal U-shaped beams
- Slabs for floors and roofs
- Floor-to-ceiling panels (With reinforcement and without reinforcement)
- Moldings
Manufacturers of cellular in Europe include YTONG, Blaublock, Hormicel, etc, in Latin American countries, for example; Retak, Lika, Airblock, Brimax, Celcon, etc. And in the United States: Aercon AAC, Megaacrete, Aircrete, etc.
Up to this point, it seems we have a winning material for house construction, but… What are its advantages and disadvantages?
Advantages of cellular concrete
Already seeing the characteristics of aerated concrete, we can infer what benefits it offers over traditional materials used in masonry.

The main advantages of cellular concrete are:
- Low water absorption: Its structure with high air content reduces water absorption.
- Fire resistance: Tolerates high temperatures without breaking or exploding. Fireproof – FR 180.
- Durability: Long-lasting material, resistant to decay and time.
- Thermal insulation: It has low thermal conductivity, meaning it is an excellent insulator for both cold and heat.
| Type of construction material | Thermal conductivity coefficient λ (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| Cellular concrete | 0.16 (Blocks between 0.89 to 0.14) |
| Fibrocenter | 0.22 |
| Woods, boards | 0.23 |
| Plaster – Cardboard | 0.24 |
| Industrial brick | 0.79 |
| Adobe | 0.90 |
| Reinforced concrete | 1.63 |
? Note: The article on properties of insulating materials is of interest.
- Quick assembly and ease of cutting: Lightweight and easy to handle, with simple cutting of the pieces. Construction is accelerated.
- Acoustic insulation: High sound absorption, improves comfort in buildings.
- Speed in construction: Due to the dimensions of the pieces (8 pieces x m2), the reduction of other masonry operations, and the possibility of easy cutting, construction on site is expedited.
- Clean finishes and no waste: The finishes are clean and fine. And with the ease of cutting, material waste is reduced.
- Sustainable material: Its environmental impact is low, similar to that of wood.
- Water vapor permeability: Good behavior against resistance to water vapor diffusion.
- Compression resistance: It is possible to use prefabricated elements – blocks – as load-bearing walls or in slab elements, that is, structural use (Recommended maximum two floors, although the calculator will determine the needs).
Compression resistance of cellular concrete block between 3 MPa and 5 MPa (megapascals), reinforced concrete between 20 MPa and 40 MPa
- Ease of transport and weight reduction: Its low weight facilitates the transport of prefabricated elements, but also reduces the weight of masonry or structural.
It should be noted that if the entire construction is load-bearing with pieces and cellular concrete block, the building’s load is reduced by tens of tons, which decreases the size and cost of the foundation.
Wait! We need to see the disadvantages of cellular concrete…
Disadvantages of cellular concrete
Every material and construction system has its obstacles and disadvantages. The ones we most appreciate when talking about building a house with lightweight cellular blocks:

- Unskilled labor: Construction workers and masons are used to building with the traditional system. Specific training is needed, although the construction system is simple.
- Limitations in structural applications: Although factory pieces perform well in compression, they have their restrictions when compared to reinforced concrete.
- Few material suppliers: We already know that competition is healthy, it improves prices, distribution, ease of access to material, etc.
- Less standardization among manufactured products: In traditional construction, it is easy to find, for example, the same product/prefabricated made by different companies. In cellular, we practically have to start and finish the work with the same material supplier – brand.
- Use of specific bonding material, anchors, and tools: The elements needed to build, for example, an exterior block wall, are specific. Especially the bonding material, although little is needed.
- Less construction flexibility: If we deviate a bit from the “construction standard,” we will have to combine with other traditional construction systems.
- Avoid direct contact with steel – reinforcement: Due to the composition of cellular concrete, the reinforcement cannot be in contact to avoid corrosion. In reality, any well-executed work should not present any problems.
? Note: Remember that the composition of cellular concrete can vary, even without adding “lime” to avoid possible corrosion with the reinforcement, in fact, there are lintels and slab pieces that have reinforcement.
Now where we enter into debate… What happens if we compare construction systems?
Comparison Cellular concrete VS Traditional construction
First, if it is already difficult to compare costs between types of conventional construction (each construction is a world), it is even more compelling when we compare “apples and oranges,” that is, cellular block partitions with other traditional competitors.
From here. The following table shows us a comparison between walls with cellular block, hollow thermo-clay block, and ceramic brick wall + ETICS system:
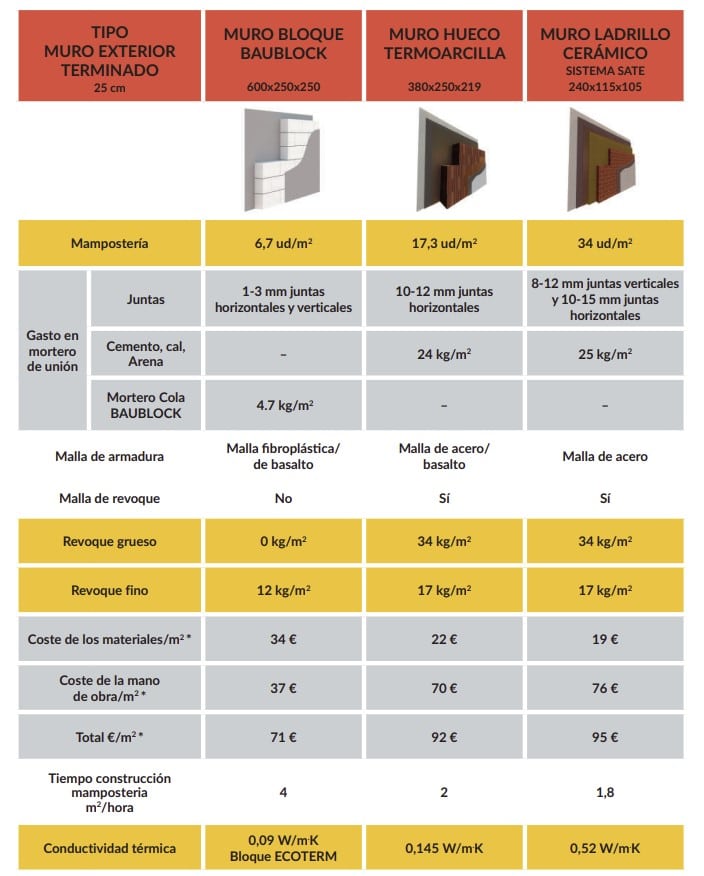
From the comparison, we see that the winner in price/m2 is cellular concrete for exterior partition, which also has a much lower thermal conductivity than its competitors. If we break it down a bit more:
| Type | Cellular block wall | Hollow thermo-clay block wall | Ceramic brick wall + ETICS system |
|---|---|---|---|
| External walls | Homogeneous structure, stability, no additional thermal insulation required, easy cutting | No thermal insulation required, fragile material that can be damaged, prone to insects | Little variety of shapes, needs thermal insulation, high cost with rock wool |
| Interior partitions | Application of thin mortar layer, no need for thick mortar | Needs plastering with thick and thin mortar | Needs plastering with thick and thin mortar |
| Door and window openings | Allows designing high-quality openings, easy cutting with hand tools | Needs prefabricated reinforced concrete lintels or metal bars | Needs prefabricated reinforced concrete lintels or metal bars |
| Groove openings | Easy cutting, can be done with hand tools | Requires diamond drills, fragile material that breaks easily | Very hard material, requires diamond bits |
| Final finish of the inner face | Low labor input | High labor input, long execution time | High labor input, long execution time |
| Final finish of the outer face | Any type of finish, only requires cleaning of adhesive mortar residues | High labor input, requires plastering over metal mesh | High labor input, requires plastering over metal mesh |
| Need for labor | Very low | Very high | High |
| Material price | Intermediate | Low | High |
| Overall cost | Low | Intermediate | High |
? Note: The above information belongs to the manufacturer Blaublock from this PDF.
PRICE IN SPAIN: But… What happens if I want to achieve the same insulation with traditional construction? What is the price per m2? Here, we need to consult official price bases and compare the total thermal transmittance (U = 1/∑R – See thermal wall insulation) between facade walls:
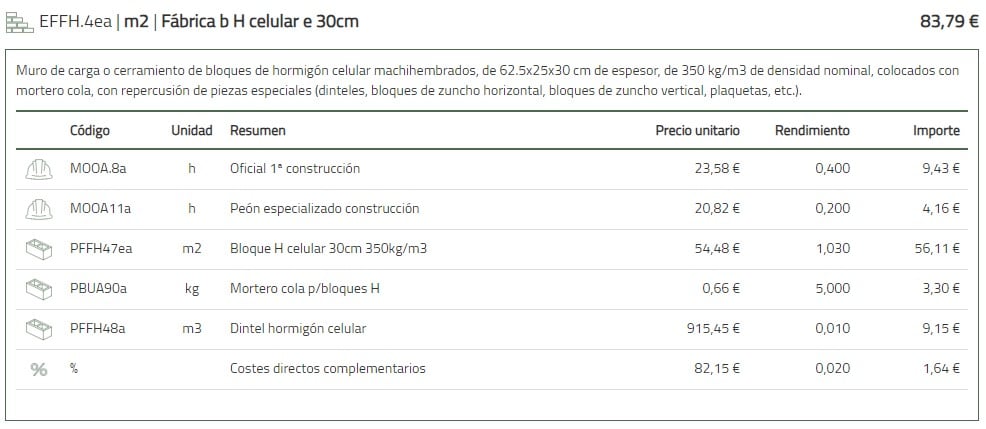
- Cellular concrete block factory (Code: EFFH.4). Thermal transmittance U = 0.34 W/ m2 ºK. Thickness 30 cm ➡️ The price of cellular concrete is 83.79 Euros/m2 for constructed and finished partition.
- IVE Price (Valencian Institute of Building) consult from HERE.
- Brick factory with interior insulating chamber (Code: EFCC.5). Thermal transmittance U = 0.38 W/ m2 ºK. Thickness 27 cm ➡️ The price is 118.52 Euros/m2 for constructed and finished partition.
- IVE Price (Valencian Institute of Building) consult from HERE.
Now, for similar insulation in an exterior wall, we can already confirm that, economically according to data from the IVE price base, cellular concrete blocks are again winners.
So… If I build a house with prefabricated cellular concrete, will it be cheaper? Well, YES and NO. The work is much more complex than simple calculations, remember!
In house construction, many factors intervene to determine the final price of the work. It will be the project, the calculations, the architect, etc., who will finally determine if it is your best option
We only have one point left to review… How is a house built with lightweight concrete block?
House construction with cellular concrete block
On the one hand. To see the entire process of house construction with cellular concrete, it is better to watch the following video that is well explained:
Constructively speaking, in my opinion, it is certainly a pleasure to see the simplicity with which the exterior walls are executed, the possibility of cutting the pieces with a handsaw, or that it can act as a load-bearing wall (structural element for low height).
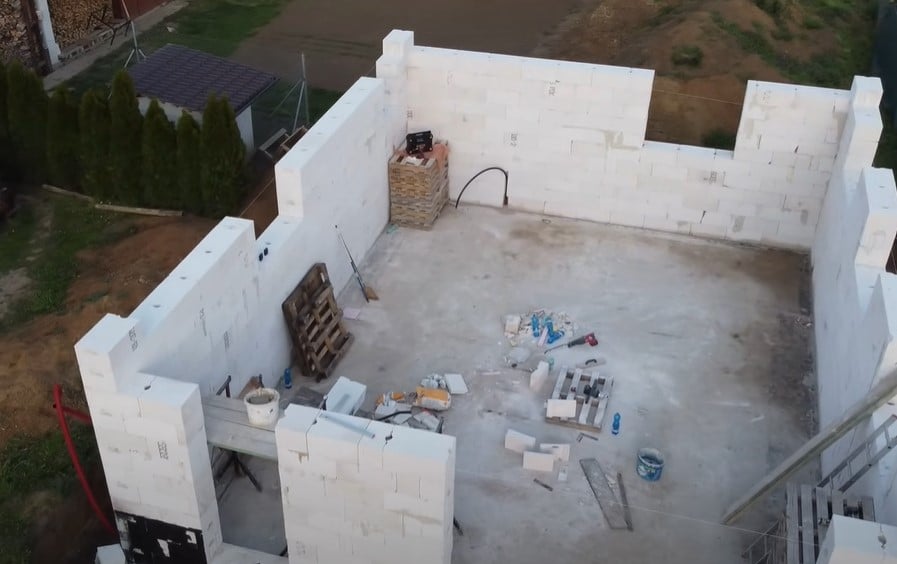

The following PDF documents explain quite well the construction details and joints you may encounter when executing works with cellular concrete pieces:
- Technical guide cellular concrete YTONG from HERE. (Very interesting section Technical Building Code for Spain)
- Manual of Hormicel from HERE.
- Technical guide for construction with cellular concrete from Retak from HERE.
- Technical manual for manufacturing and marketing HCCA bricks from Brimax from HERE.
Although in Spain this construction system is being talked about more lately, in Northern Europe or Latin America it is much more widespread.
In reality, AACC was created by a Swedish architect, J.A. Eriksson, in 1924 (three years later the autoclave curing – AACC), so it has many years of life. And remember that innovative materials for construction keep appearing.
If you liked the article, share it!