How to solve condensation moisture
Those small droplets of water that usually appear on windows and walls inside the house, is condensation moisture. It is a serious issue and can also lead to health problems.
But… Why is there humidity in the house? It is produced when the hot and humid air of the environment meets a cold surface, the water vapor condenses in drops, as when a mirror fogs up when we take a shower.
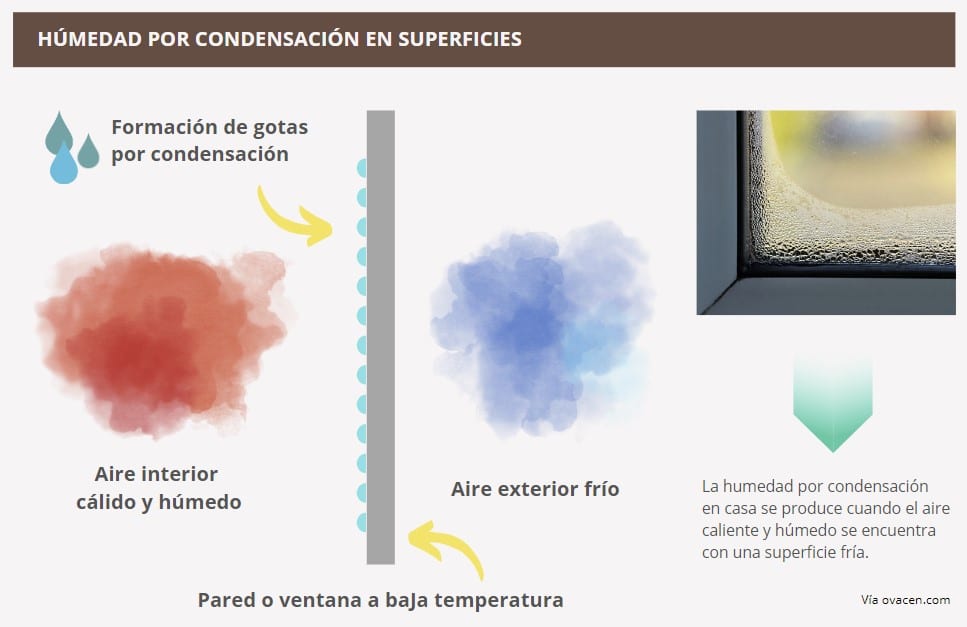
Remember: the best way to remove humidity in the house from condensation is a combination of measures, especially ventilation
Humidity on walls is an issue we need to resolve… Why is it important to solve it? Dampness in the house causes several problems over time:
- Deterioration of the home: Mold, efflorescence, stains and discoloration on walls, peeling paint, etc.
- Health problems: It affects air quality and could lead to allergies, asthma, irritations, respiratory diseases, etc.
- Bad odor: A damp environment is ideal for the proliferation of bacteria and fungi, which generate an unpleasant smell.
- Discomfort: Condensation in the air hinders perspiration and increases the feeling of cold.
? In fact, the WHO (World Health Organization) reiterates in its document on “Guidelines for indoor air quality: dampness and mold” the dangers of respiratory infections.
But… How can you tell if it’s humidity from condensation or from wall leaks? A simple home trick is to place a sheet of aluminum foil against the wall and see where it gets damp:
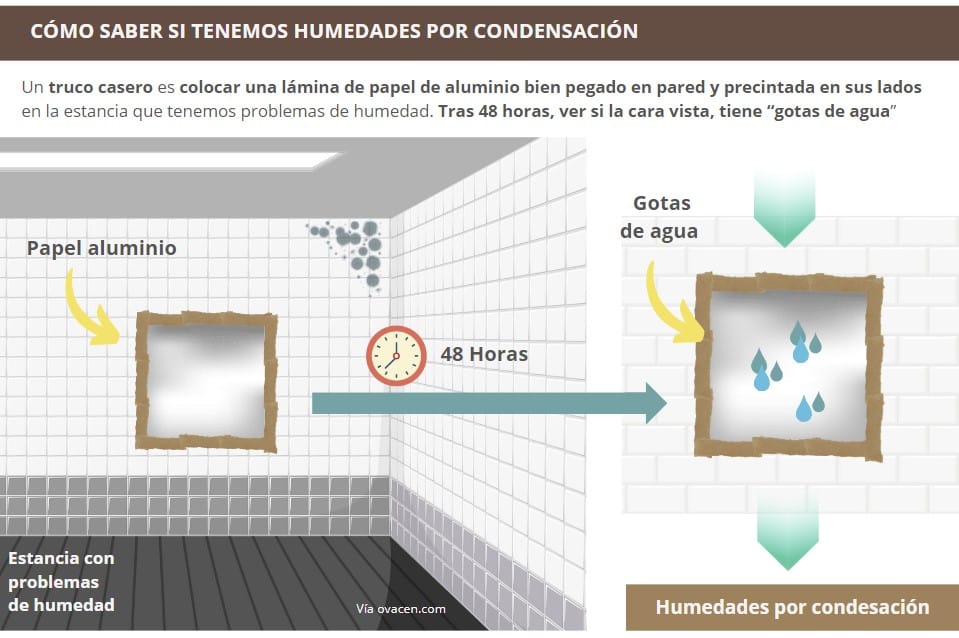
Once it’s clear. Then… What solutions are there to reduce condensation damp?
1.- Ventilating every day eliminates condensation moisture
Although we insist on this topic, you must ventilate the house periodically for about ten minutes to improve air quality. It’s very effective!
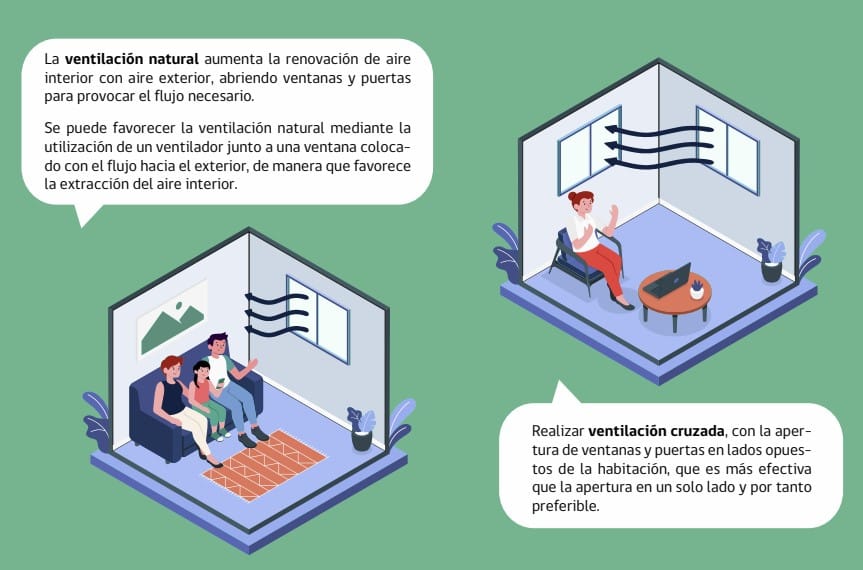
A humid environment needs to regenerate the air, and natural ventilation is perfect for eliminating humidity in the house. But always keep in mind that:
- We cannot ventilate when it’s raining or immediately after, the air is saturated with humidity.
- The ventilation must be cross ventilation, just opening one window is not enough!
- Open doors of all rooms, especially humid areas like bathrooms, kitchen, laundry room, basement, etc.
Cross ventilation is necessary to avoid dew humidity, that is, opening windows or doors on opposite sides of the house
? Note: In cold or humid climates, ventilation may not be enough to control humidity on walls and ceilings from condensation. In these cases, it is advisable to use a dehumidifier or thermal insulation (See both cases later).
2.- Expel steam while cooking
The vast majority of foods we consume daily need to be boiled or prepared with water. The kitchen generates significant amounts of steam.
That hood or smoke extractor in the kitchen that you don’t want to activate because it consumes too much electricity ends up being detrimental, it is a solution to reduce condensation moisture while cooking.
It is estimated that, on average, cooking releases 0.5 kg of water vapor per hour into the environment. Keep that in mind!
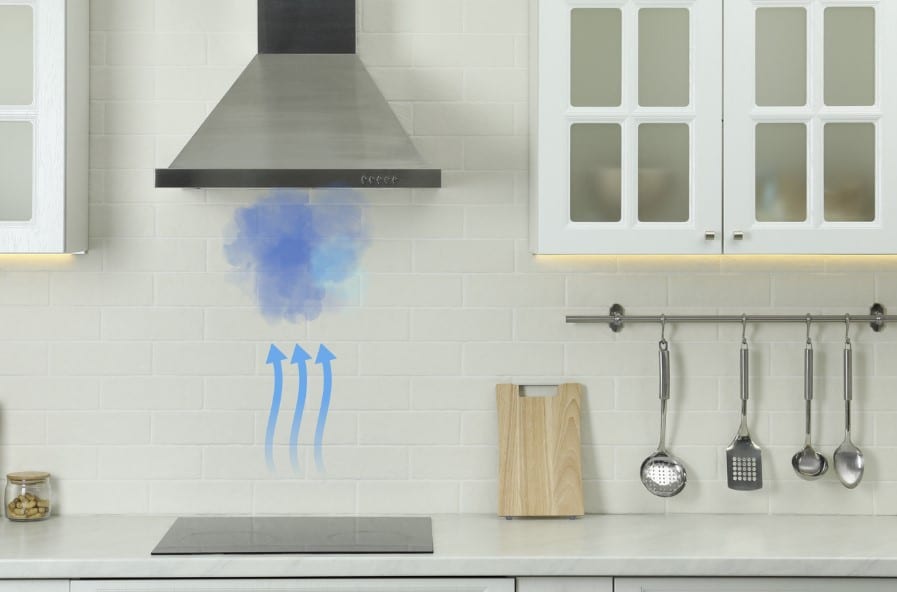

To avoid condensation damp in kitchens you should activate the smoke extractor when cooking, but you can also take the following measures:
- Cook with the windows open or use a smoke extractor.
- Cover pots and pans while cooking.
- Do not overfill pots with water if it’s not necessary.
- Use a pressure cooker to cook food, they control water vapor better.
- Ventilate the kitchen after cooking.
3.- Washing, drying, and ironing activities produce humidity
To be clear, drying or ironing clothes can generate more vapor than washing itself. Take note!
Although we may not be aware, wet clothes contain a large amount of water. In fact, when we have used the washing machine and it has spun, the clothes can store up to 1.5 times their weight in water.
After a spin cycle in the washing machine, clothes can store up to 1.5 times their weight in water

Anything related to laundry is better done outdoors or in a well-ventilated environment, it prevents humidity from accumulating on walls and ceilings. Some additional tips are:
- Wash clothes in the washing machine with the room door open.
- Dry clothes outdoors or with a dryer that drastically reduces the wetness of clothes. They work great!
- Iron clothes in a room with open windows and cross ventilation.
4.- Ventilation system in the bathroom to avoid condensation damp
The bathroom is one of the most humid areas of the home. When we bathe with hot water, especially in showers, a large amount of vapor is released that condenses on walls and ceilings.
This sudden thermal change causes the bathroom window, mirror, or screen to fog up due to condensation. It is estimated that a bathroom can generate a rate of 1kg of water vapor per hour.
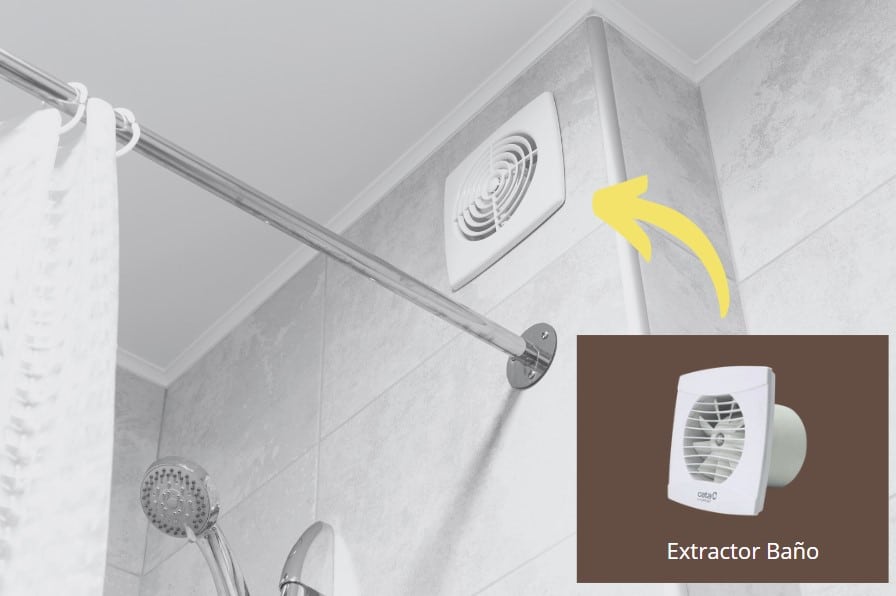

We should always have a ventilation or forced air extraction system in the bathroom to avoid condensation from humidity.
Without a window and only with a small ventilation grille, usually in the long term, we will have mold that slowly appears in joints, corners, and even on the ceiling. Tips to follow:
- Although many bathrooms and toilets have a ventilation grille to avoid humidity from condensation, it is often not enough. A small air extractor will need to be installed in the bathroom.
- After a bath or shower, the door should remain closed (open the bathroom window), we don’t want the dew in the environment to pass into the house. After a few hours, open the door to start the cross airflow from the hallway to the window or ventilation grille.
- Long showers and baths, no, please! Besides needing to save water, it exponentially increases vapor in the air.
At this point, be careful with anti-humidity paints, anti-mold primers, etc., they are to tackle problems from capillarity/leakage “from outside”, they do not solve the root of the problem, as the humidity will remain inside.
? Note: The “dew point” is a term used to describe the temperature at which water vapor in the air condenses to form dew.
5.- The house is not a gym
Having a “sports room” at home is a bad idea. People continuously generate vapor through our breathing and perspiration.
If we perform sports activities at home or continuous work efforts, we increase the amount of water vapor in the environment. It’s no joke!
In the following table, we can see the water vapor produced by a person according to activity:
| Water vapor (g/h) produced by a person of average build according to temperature | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTIVITY | 10°C | 15°C | 20°C | 25°C |
| Rest | 36 | 36 | 45 | 66 |
| Light work | 54 | 72 | 110 | 175 |
| Normal work | 66 | 120 | 170 | 205 |
| Very heavy work | 155 | 215 | 300 | 350 |
To avoid condensation moisture, everything counts here. Either we have a properly ventilated gym room or we exercise outdoors.
6.- Do not have too many plants inside the house
It’s okay to have some plants at home, but not a “jungle”. Indoor plants transpire water, which increases the moisture in the air.
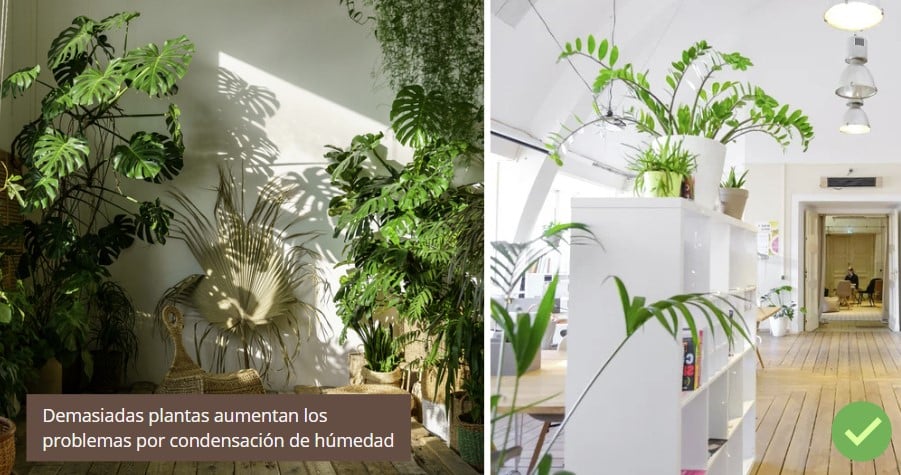

If you have humidity problems, it is advisable to keep as few plants as possible inside the house. Some tips:
- Choose indoor plants that do not transpire much water. Examples include tillandsia, aloe vera, jade, succulents, African violets, etc.
- Place the plants in a well-ventilated area.
- Water the plants moderately.
7.- Be careful with heating and certain appliances that produce humidity
Dampness from condensation mainly occurs in winter, there are sharper contrasts between the warm, humid air in the room meeting cold windows and exterior walls.
From here, heating can increase humidity from condensation in several ways:
- When we increase the ambient temperature: Warm air is less dense than cold air, so it can retain more water vapor than cold air.
- If we reduce ventilation: When the heating is turned on, we tend to close the windows to keep the heat inside the house. This reduces ventilation and increases the damp air.
- Certain heaters generate water vapor: Open flame heaters – without a chimney/smoke extraction – such as a paraffin, bioethanol, butane combustion stove, etc., generate water vapor through combustion (They use hydrocarbons, which contain hydrogen that combines with the oxygen in the air and produce water).
?Advice: To prevent condensation avoid large temperature jumps when using heating due to how warm and cold air interacts with humidity. It’s better to maintain a constant temperature of 18 – 19ºC and increase to 20-21ºC, rather than radical changes from 16ºC to 22ºC.
8.- Using a dehumidifier prevents condensation
The dehumidifier does not solve the root problem, which is usually due to our bad habits, but it is an effective device.
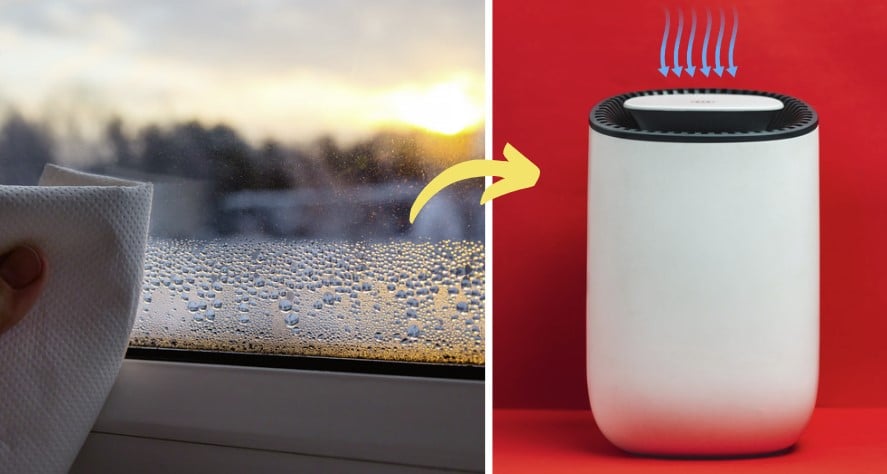

Starting from this point, a dehumidifier is a portable electric device that helps reduce air humidity in a closed space. But… How does it work?
- The humid air enters the dehumidifier through a fan.
- The air passes through a cold coil. This coil condenses the water vapor from the air, turning it into liquid water.
- The liquid water is deposited in a tank or is directly drained.
- The dry air is reintroduced into the room through another fan.
An air conditioner can function as a dehumidifier when set to “DRY or DEHUMID” mode
In reality, an air conditioning unit can function as a dehumidifier when set to “DRY or DEHUMID” mode, and you don’t have to buy the device.
? Note: There are natural solutions that help absorb humidity from the air, such as placing containers with baking soda, charcoal, or coarse salt.
Some tips discussed and others in the following video:
9.- Improving the thermal insulation of walls prevents condensation moisture on walls
So far, we have focused on reducing indoor air humidity. Now, we focus on preventing exterior-facing walls from getting too cold… How?
Improving the thermal insulation of walls is key, but its intervention is much more complex and technical. Additionally, there are a lot of insulating materials:
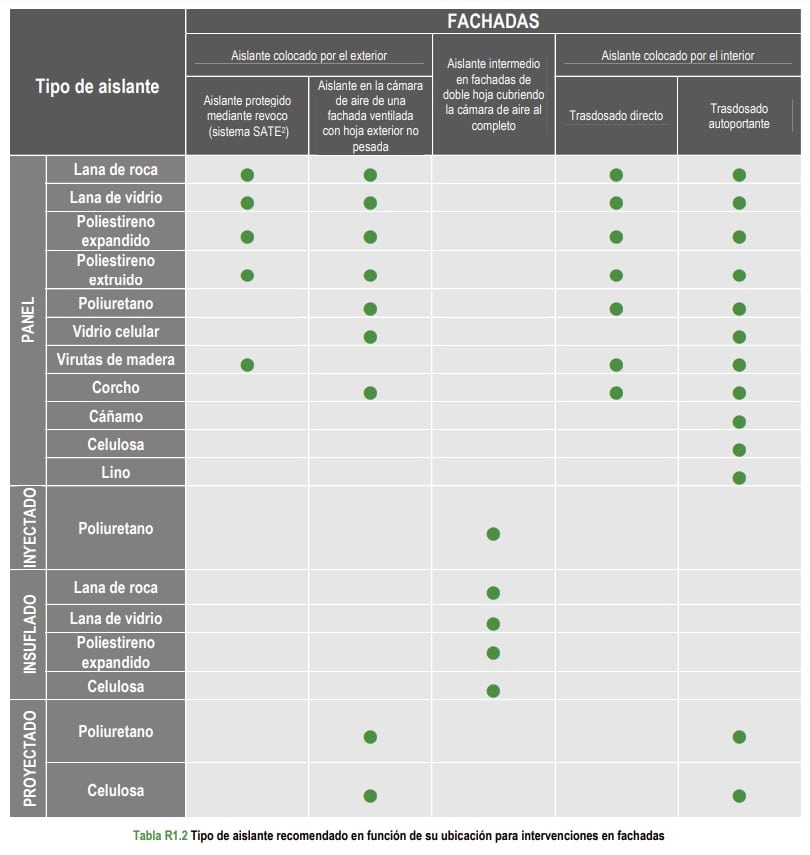
There is a wide range of products, with variations in the characteristics and properties of insulating materials according to the specific needs of each use in condensation damp on walls, ceilings, and floors.
Here, a significant financial investment is required, and hiring professionals for its execution is necessary. Remember! We have three options:
- Interior insulation: Installed inside the house. Although there are several systems, mineral wool or glass panels are usually installed with rails attached to the wall, plus a layer of gypsum board covering.
- Exterior insulation: Installed outside the house, for example, on the facade. It involves applying an insulating coating composed of several layers, protected by mortar. The most effective system!
- Blown-in insulation: An insulating material is injected into the air cavity within the wall, if it has a cavity. It is cleaner than other systems, but it cannot always be done.
Improving the thermal insulation of walls is an investment that brings benefits. It reduces condensation and humidity, improves the energy efficiency of the house, and increases interior comfort.
If you liked the article, share it!
